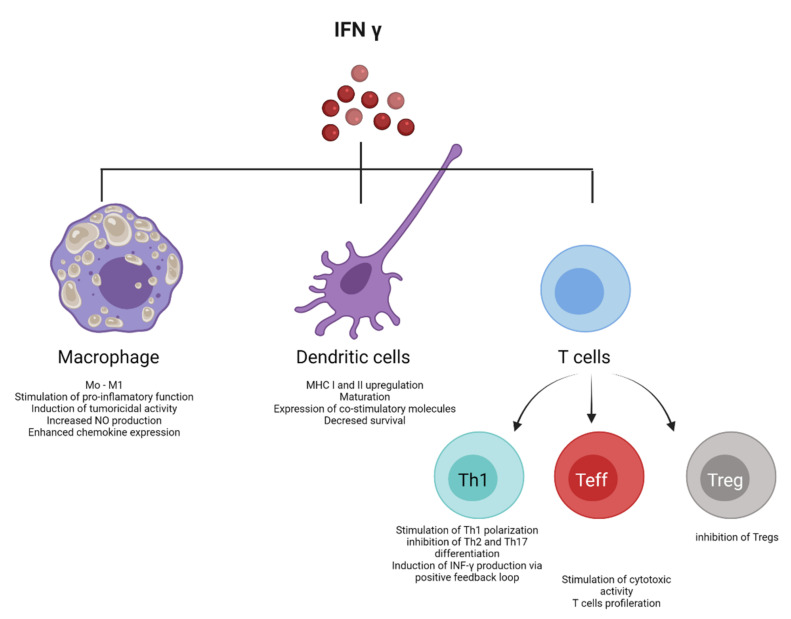
Figure 6.
Role of IFN-γ in the antiproliferative response. Interferon-γ interacts with various cells in a tumor microenvironment to initiate the production of the cytokine itself. Some of these cells are T lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Macrophages: the protein stimulates the polarization of macrophages towards a proinflammatory phenotype by increasing the secretion of chemokines. Dendritic cells: increases the maturation of these cells, positive regulation of MHC I and II with increased IRF1 expression, and decreased IFN-γ-dependent dendritic cell survival. T cells: stimulates their differentiation with Th1 polarization. IFN-γ causes positive feedback, increasing their production in Th1 cells and inhibiting differentiation towards Th2 and Th17. Maturation of virgin T cells to effector CD8 + T cells requires IFN-γ. IFN-γ is the primary cytotoxic molecule secreted by these cells. IFN-γ inhibits immunosuppressive regulatory T cells. Created with BioRender.com.