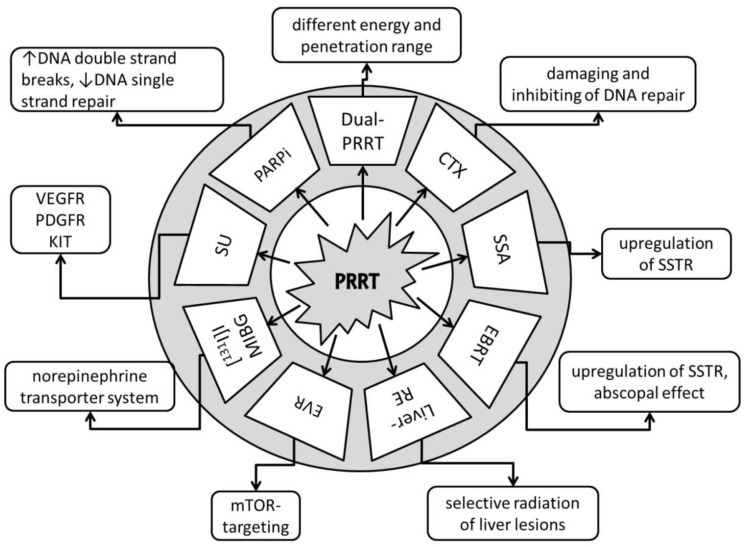
Figure 2.
Anti-tumor effects of combination partners of PRRT. Dual-PRRT = dual-radionuclide peptide receptor therapy: a combination of different energy and penetration range levels to better target metastatic lesions with different sizes and nonhomogeneous somatostatin receptor (SSTR) distributions [19,20]. CTX = chemotherapy: damaging and inhibiting DNA repair, cell proliferation arrest, tumor cell reoxygenation, and synchronization of the cell cycle or apoptosis [21]. SSA = somatostatin receptor analogues: upregulation of SSTR, increasing number of targets for PRRT [22]. EBRT = fractionated external beam radiotherapy: upregulation of SSTR, increasing number of targets for PRRT, potential abscopal effect with triggering of immuno-mediated antitumor effects [23,24]. Liver-RE = liver radioembolization: selective radiation of liver tumor lesions; potential abscopal effect with triggering of immuno-mediated antitumor effects [25,26]. EVR = everolimus: targets the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), with growth-inhibitory and anti-angeogenic effects [27,28]. [131I]I-MIBG = [131I]I-metaiodobenzylguanidine: targets the norepinephrine transporter system [29]. SU = sunitinib: tumor growth arrest via targeting of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGFR), and receptor tyrosine kinase KIT [30]. PARPi = poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitors: increases DNA double-strand breaks; blocks DNA single-strand repair [31].