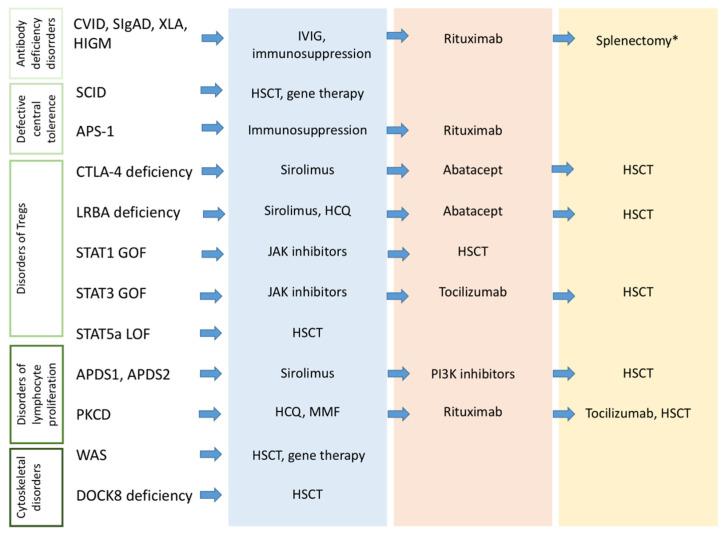
Figure 2.
Therapeutic strategies for autoimmunity in patients with PIDs. The figure shows the current therapeutic options for specific PIDs. The choice of the therapeutic strategy (immunosuppressive agents, biologic drugs, HSCT, gene therapy) depends on the clinical severity, comorbidities and also on the availability and physician’s experience. * In patients with refractory autoimmune cytopenia. APDS: Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase d syndrome; APS-1: Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome 1; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic lymphocyte antigen 4; CVID: Common variable immunodeficiency; HCQ: Hydroxychloroquine; HIGM: Hyper-IgM syndromes; HSCT: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; JAK: Janus kinase; LRBA: LPS-responsive beige-like anchor protein; MMF: mycophenolate mofetil; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKCD: protein kinase C δ deficiency; SCID: severe combined immunodeficiency; sIgAD: selective IgA deficiency; STAT: Signal Transducers and Activator of Transcription; Tregs: regulatory T cells; WAS: Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome; XLA: X-linked agammaglobulinemia.