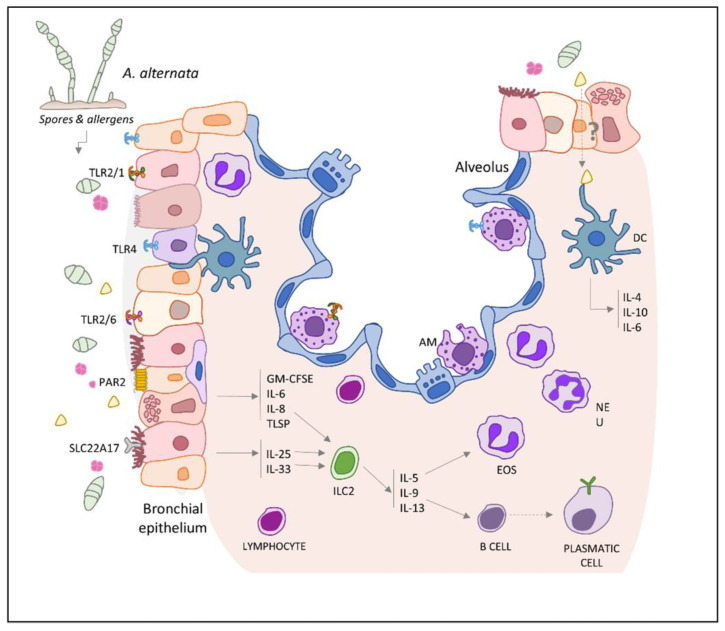
Figure 2.
Immune responses induced in airway epithelium by Alternaria alternata. Spores and mycelium fragments containing allergenic compounds (such as Alt a 1) can reach upper airways, where they can interact with TLRs (TLR2, TLR4), PAR 2, or SLC22A17 receptors present in the alveolar macrophages and epithelial cells. The activation of these types of cells induces proinflammatory responses by means of the production of alarmins (IL-33, IL-25, TSLP) and other proinflammatory cytokines. Alarmins promote the recruitment and activation of innate lymphoid cells type 2 (ILC2), which have an important role in the development of Alternaria-induced type 2 responses (e.g., eosinophil infiltration, mucus hypersecretion, airway hyperreactivity, IgE production, etc.). EOS, eosinophil; NEU, neutrophil; DC, dendritic cell; AM, alveolar macrophage.