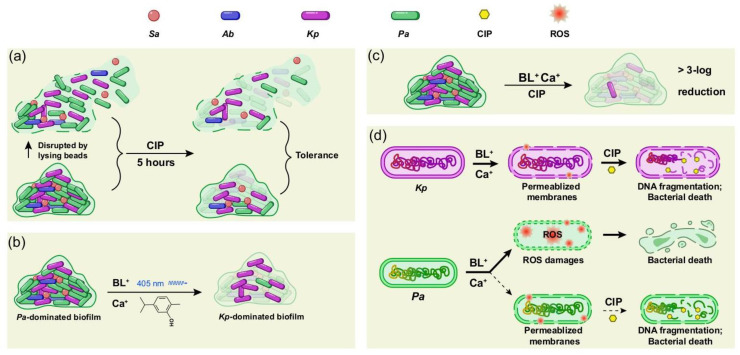
Figure 4.
Schematic diagrams of anti-biofilm modalities. (a) Intact biofilm or disrupted biofilm showed similar tolerance to ciprofloxacin (CIP). (b) P. aeruginosa-dominated biofilm became K. pneumoniae-dominated after BL-Ca dual treatment. (c) The cocktail therapy of 80 J/cm2 BL, 125 µg/mL Ca, and 10 µg/mL CIP showed strong anti-biofilm activity against the four-species biofilm. (d) BL-Ca treatment compromises the bacterial outer/cytoplasmic membranes of K. pneumoniae and allows entrance of CIP into the cells. CIP induces DNA fragmentation and cell death. Unlike K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa is mainly killed by ROS overwhelmingly induced by BL-Ca dual treatment. Bacteria survived the treatment could be further killed by CIP that enters the cells sufficiently following BL-Ca treatment. Sa: S. aureus; Ec: E. coli; Kp: K. pneumoniae; Ab: A. baumannii; Pa: P. aeruginosa.