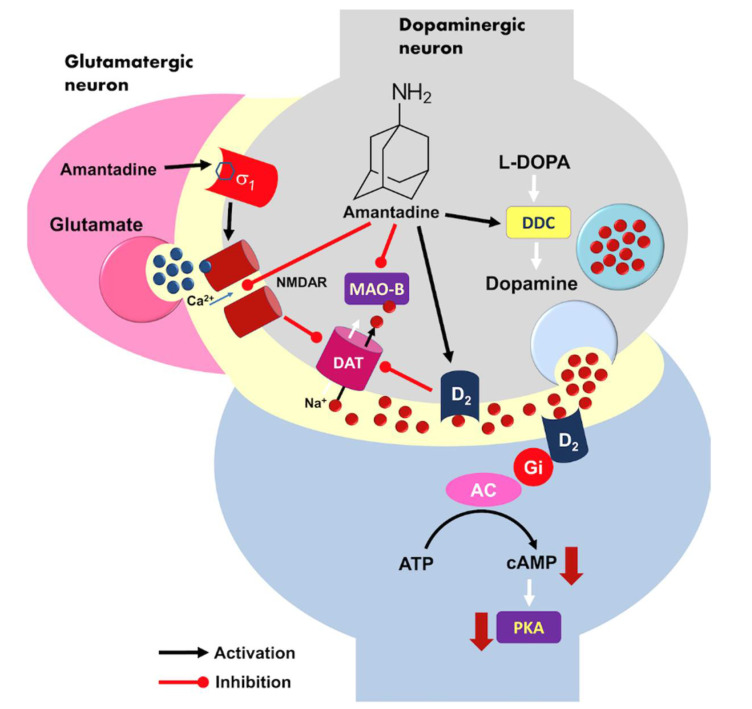
Figure 1.
A model of possible molecular mechanism of amantadine action at the level of brain dopaminergic signaling. Activation of presynaptic dopamine receptor D2 may reduce dopamine transporter 1 (DAT1) activity in response to high neurotransmitter and elevates dopamine level within synaptic cleft. D2 is a Gi-coupled receptor, its excitation causes an inhibition of the adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity, decreased cAMP production and finally silencing of protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent neuronal signaling pathway. Amantadine is also able to inhibit monoaminoxidase B (MAO-B) but it does support L-DOPA decar-boxylase (DCC) activity in the presynaptic neuron. DDC—L-DOPA decarboxylase; MAO-B—monoaminoxidase B; DAT—dopamine transporter; AC—adenyl cyclase; PKA—protein kinase A.