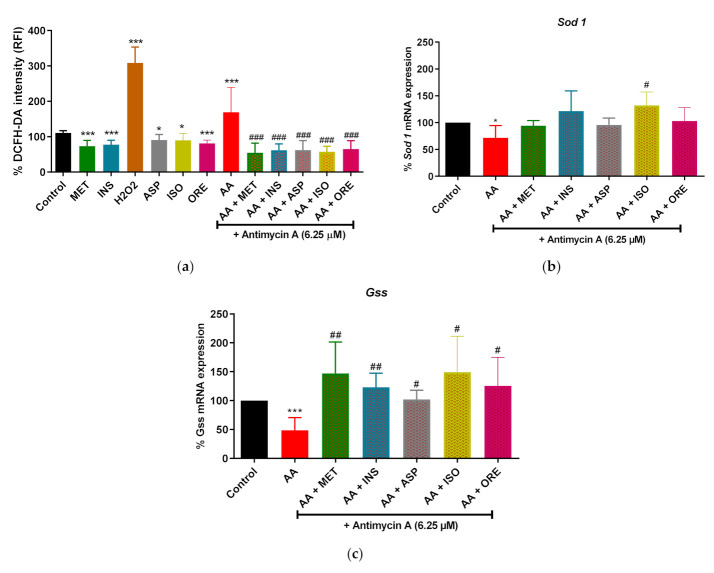
Figure 2.
The impact of aspalathin, isoorientin, and orientin on the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (a) and the expression of antioxidants genes such as superoxide dismutase 1 (Sod1, (b)) and glutathione synthetase (Gss, (c)) in cultured C2C12 myotubes following the exposure to antimycin A. Briefly, C2C12 cells were treated with antimycin A (6.25 µM) for 12 h to induce mitochondrial dysfunction. Thereafter, cells were treated with aspalathin (Asp), isoorientin (Iso), orientin (Ore) (10 µM), and comparative control metformin (Met) (1 µM) for 4 h. Insulin (Ins) (1 µM) and H2O2 (1000 µM) (ROS positive control) were added for 30 min. Results are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 versus normal control; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 versus antimycin A control. Dichlorofluoresceine-diacetate (DCFH-DA) green fluorescence stain (intensity) was used as a measurement of ROS production.