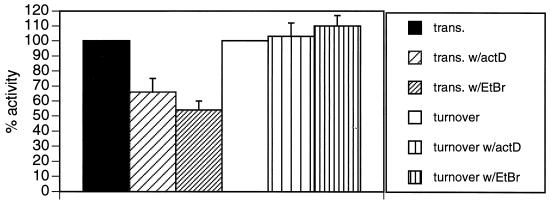
FIG. 7.
Effects of transcriptional inhibitors on RNA synthesis and UTP-dependent turnover of mitochondrial polyadenylated RNAs. To measure the effects of transcriptional inhibitors on in organello poly(A)+ RNA synthesis (trans.), mitochondrial vesicles were labeled with [α-32P]CTP for 10 min in the absence or presence of actinomycin D (50 μg/ml) or ethidium bromide (20 μg/ml). The inhibitors were added 10 min prior to the addition of nucleoside triphosphates. Incorporation of [α-32P]CTP into poly(A)+ RNA was determined. To measure the effect of transcriptional inhibitors on UTP-dependent poly(A)+ RNA turnover (turnover), mitochondrial vesicles were labeled with [α-32P]CTP for 10 min and chased for 65 min in transcription buffer containing 2 mM CTP and 0.1 mM UTP. Actinomycin D (50 μg/ml) or ethidium bromide (20 μg/ml) was added directly to the chase reaction mixtures. Incorporation of [α-32P]CTP into poly(A)+ RNA was determined. To calculate UTP-dependent turnover, the amount of poly(A)+ RNA degradation observed in the absence of UTP was subtracted from the amount observed in the presence of UTP. The amount of transcription or UTP-dependent RNA turnover observed in the absence of drug treatment was defined as 100% activity. Error bars represent 1 standard deviation.