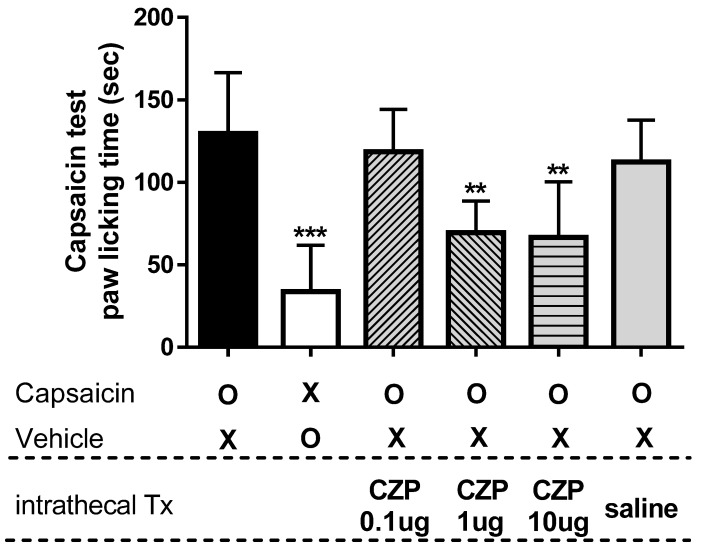
Figure 2.
The graph shows the paw-licking time after intrathecal capsazepine administration in a mouse model of capsaicin-induced spontaneous pain. Intraplantar injection of capsaicin (capsaicin, n = 6) induced paw-licking behavior characteristic of nociception, while saline-injected animals (Vehicle, n = 6) exhibited significantly less paw-licking behavior compared to capsaicin-injected animals (*** p < 0.001). Doses of 1 and 10 μg of capsazepine (CZP 1 μg and CZP 10 μg, n = 6, respectively) significantly suppressed capsaicin-induced paw-licking time compared to that in capsaicin-injected mice (** p < 0.01), whereas a dose of 0.1 μg of capsazepine (CZP 0.1 μg, n = 6) and intrathecal administration of sterile saline (saline, n = 6) did not result in significant changes in paw-licking time.