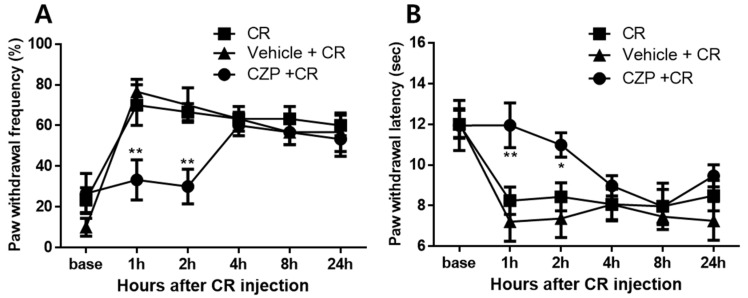
Figure 3.
Graphs show the anti-nociceptive effects of intrathecal administration of 1 μg of capsazepine on mechanical allodynia (A) and thermal hyperalgesia (B) in mice with carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain. Carrageenan-induced mechanical allodynia at 1 and 2 h was significantly suppressed in the capsazepine-administered group (CZP + CR, n = 8) compared to that in mice with carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain (CR, n = 8). For thermal hyperalgesia, paw withdrawal latency increased from 1 to 2 h after carrageenan injection compared to that in carrageenan-injected mice (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). No significant differences in paw withdrawal frequency (%) and paw withdrawal latency (sec) were observed between the vehicle group (Vehicle + CR, n = 8) and 2% carrageenan-injected animals at all timepoints of behavioral measurement.