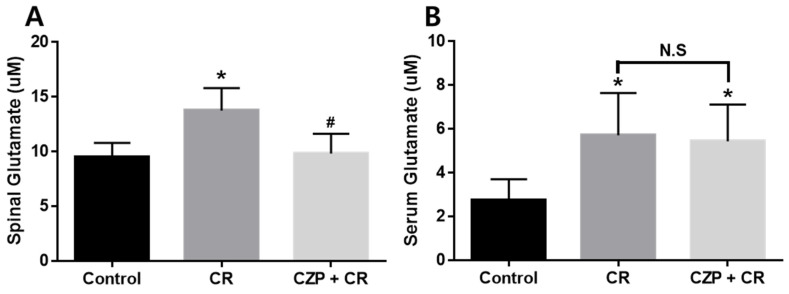
Figure 4.
Graphs show the effect of intrathecal capsazepine treatment on the suppression of glutamate concentration in the spinal cord (A) and serum (B) of mice with carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain. Spinal glutamate concentration was significantly higher in carrageenan-injected animals (CR, n = 5) than in the control group (Control, n = 5, * p < 0.05). Glutamate concentration in the spinal cord was significantly lower in intrathecal capsazepine-treated animals (CZP + CR, n = 5) than in the carrageenan-injected group (# p < 0.05). Serum glutamate concentration was significantly higher in carrageenan-injected mice (CR, n = 5) and capsazepine-administered mice (CZP + CR, n = 5) than in control mice (Control, * p < 0.05). No significant differences (N.S) were observed in glutamate concentration between intrathecal capsazepine-treated mice and the carrageenan-treated group.