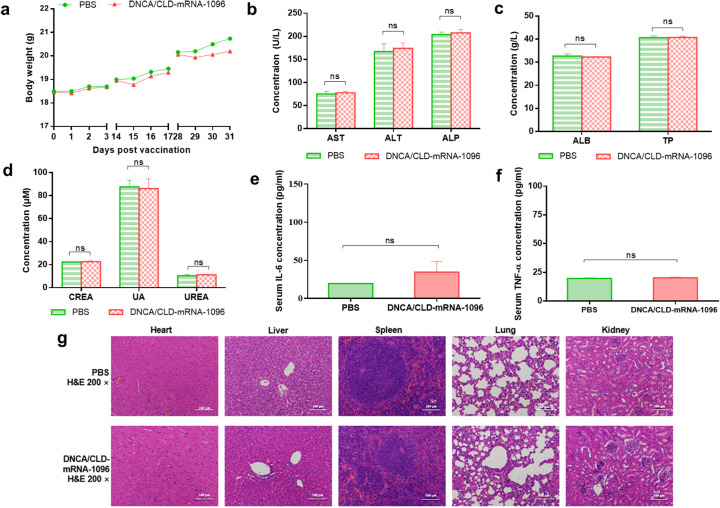
Fig. 6.
The safety evaluation of DNCA/CLD-mRNA-1096 in mice. Female BALB/c mice of 6–8 weeks old were inoculated with DNCA/CLD-mRNA-1096 (mRNA-1096 = 10 μg) or PBS via intramuscular route of administration. (a) The body weight records of mice on the first three days after each vaccination. (b-d) The liver and kidney function were determined by blood biochemical indexes (n = 5). ALT, AST, ALP, TP and ALB represented the liver function, while CREA-J, UA and UREA represented kidney function. (e-f) The immune activation effects in mice were represented by analysis of the serum proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α (n = 5). Data were shown as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated with the unpaired Student's t-test (two-tailed) for comparing the difference between the PBS and the DNCA/CLD-mRNA-1096 group (ns: p > 0.05). (g) Representative histopathology (H&E) of different tissues, heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney, in the PBS or the DNCA/CLD-mRNA-1096 group. H&E-stained sections shown in the data were one representative result of the three tested mice at 48 h post inoculation. Scale bar = 100 μm, 200 × .