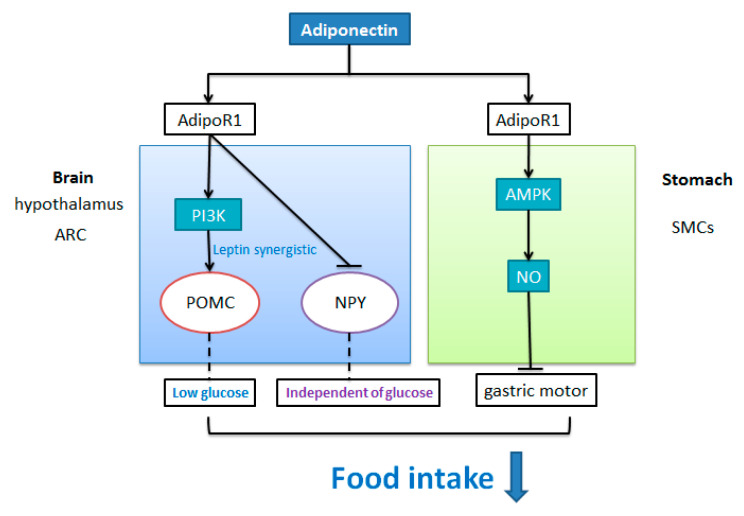
Figure 3.
The inhibitory effect of adiponectin on food intake. In the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus, adiponectin may bind to AdipoR1 in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus to stimulate the depolarization excitation of POMC neurons and inhibit the excitation of NPY/AgRP neurons, thus inhibiting food intake. The activation effect of AdipoQ on POMC neurons was closely related to low glucose concentration, PI3K and Leptin, but not to AMPK pathway. In addition, AdipoQ’s inhibitory effect on NPY neurons was independent of glucose concentration. Existing studies have in the peripheral confirmed that adiponectin can activate AMPK signaling pathway to promote NO release through binding with AdipoR1 in the basal part of the stomach, thus inhibiting food intake.