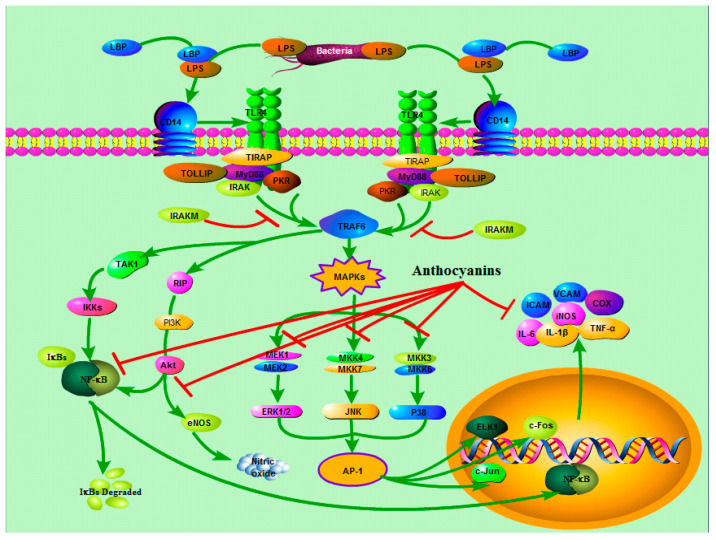
Figure 3.
Anthocyanins inhibit TLR4 protein expression and MAPKs signaling pathway. The structure of TLR4 is divided into three domains: extracellular domain, transmembrane domain, and intracellular domain. Extracellular LPS binds to CD14, and since CD14 does not have a transmembrane domain, it binds to the extracellular domain of TLR4 to a transmembrane-mediated endotoxin. When the signal was transferred into the cell, the MyD88 adaptor protein and toll–irak complex began to be recruited. The intracellular TIR region of TLR4 binds to the carboxyl end of MyD88, and the amino terminal of MyD88 binds to IRAK again to activate IRAK (IRAK-M, as a negative regulator, can inhibit the phosphorylation of IRAK and interrupt signal transduction). Activated IRAK reactivates TRAF-6 and further activates the NF-κB, MAPKs, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways, promoting the secretion of NO and inflammatory factors (Ding et al., 2018; Monica et al., 2016).