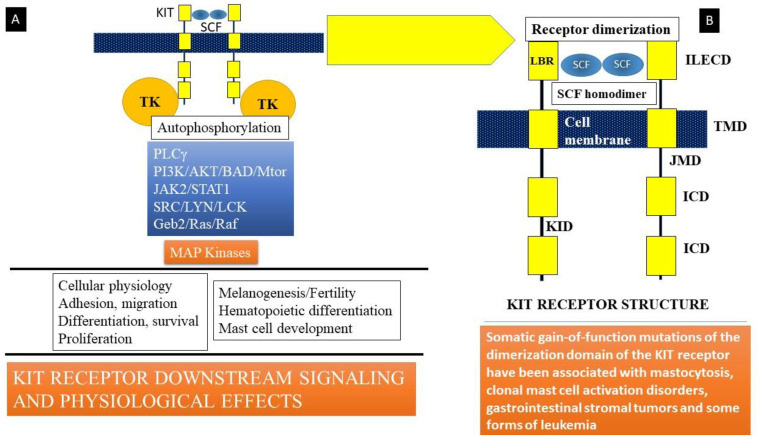
Figure 2.
(A) Stem cell factor (SCF) is a hematopoietic growth factor that binds to its receptor, KIT, a transmembrane tyrosine kinase-linked receptor on mast cells. Signaling downstream involves activation of key kinases (Phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ), protein kinase C (PKC), and linked signaling proteins: Janus kinase 2 (a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, JAK2), signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), and other signal transduction mediators). These lead to action of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAP kinase). Somatic mutations in c-KIT that code for the KIT receptor have been linked to the development of systemic mastocytosis, a clonal hematological disorder. The most common of these mutations is the D816V mutation that leads to enhanced survival and proliferation of mast cells, a feature of clonal mast cell disorders including mastocytosis and mast cell activation disorders. (B) KIT is the cellular counterpart of the v-KIT oncogene derived from a feline leukemia virus. It is encoded in the W or c-KIT locus on human chromosome 4q11-q12. KIT is composed of an immunoglobulin-like extracellular domain (ILECD), that is involved in ligand binding (LBR), an anchoring transmembrane domain (TMD), a juxta-membranous domain (JMD), and intracellular domains (ICD). KID = kinase insert domain. Binding of stem cell factor to KIT results in receptor dimerization and activation of protein kinase activity.