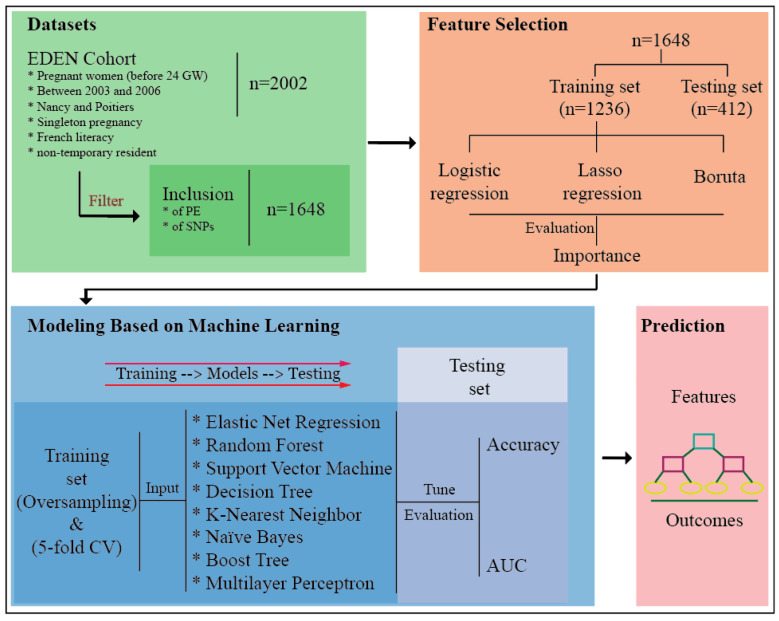
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the study. Of the 2002 pregnant women in the EDEN mother–child cohort study, 1648 satisfied the inclusion and exclusion criteria and were recruited to this study. The dataset was randomly stratified into two parts, a training set and a testing set, according to a 3:1 ratio. Three methods were used to evaluate the importance of correlated features within the training set: logistic regression, lasso regression, and the Boruta algorithm. Eight machine-learning models were built, tuned, and trained on an oversampled training set with five-fold cross-validation (CV), followed by validation on the testing set. The performance of the models was evaluated using metrics of accuracy and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). The final model was used to build a decision tree for predicting preeclampsia. GW: gestational week; PE: preeclampsia; SNPs: single nucleotide polymorphisms.