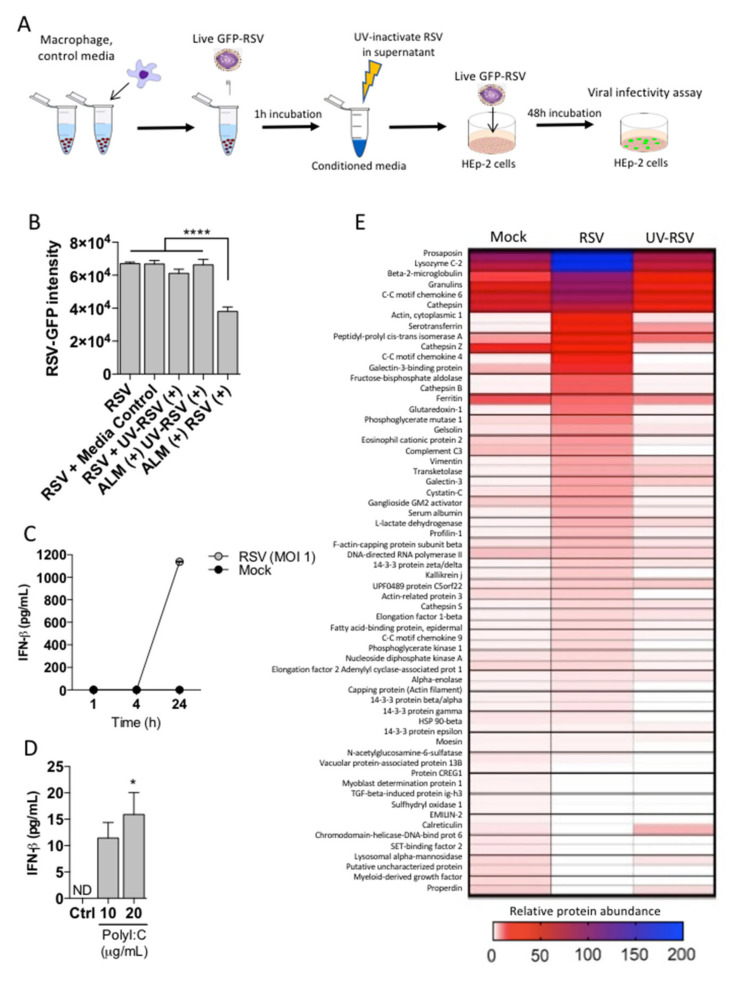
Figure 4.
ALMs confer antiviral effects through a secreted factor. (A) Technical schematic indicating the work flow to measure secreted factor in ALMs supernatants. (B) ALMs (1 × 106/mL) were exposed to RSV or UV-RSV at an MOI of 1 for 1 h. Afterwards, the supernatants were collected and UV-irradiated to neutralize residual active RSV. This was used as a conditioned media, which was then added onto previously seeded HEp-2 cells with competent RSV-GFP (MOI 1) and RSV replication was measured by GFP fluorescence. Control indicating HEp-2 cells with EMEM, media control indicates UV-irradiated EMEM, UV-RSV (+) indicates media containing UV-inactivated RSV, ALM (+) UV-RSV (+) indicates conditioned media from ALMs exposed to UV inactivated RSV, ALM (+) RSV (+) indicated conditioned media from ALMs exposed to RSV. (C,D) (C) ALMs (1 × 106/mL) were stimulated with RSV (MOI 1) or mock-stimulated for 1, 4 or 24 h at 37 °C under 5% CO2. (D) ALMs were stimulated with TLR3 ligand Poly I:C (10 and 20 μg/mL) for 24 h at 37 °C under 5% CO2. Afterwards, supernatants were collected and IFN-β concentrations were determined using ELISA. (E) ALMs (1 × 106/mL) were exposed to mock, RSV or UV-RSV at an MOI of 1 for 4 h. Afterwards, the supernatants were collected, concentrated and prepared for proteomic analysis as described in the Section 2. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments performed in triplicates and represent mean ±SEM. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (B,D). * p < 0.05; **** p < 0.0001.