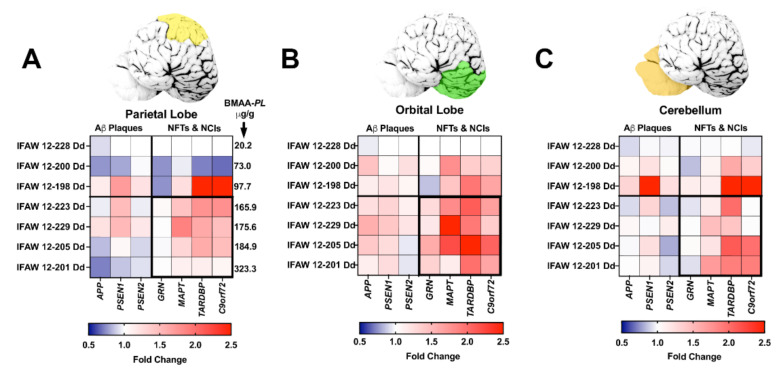
Figure 2.
Brain Region-Specific Analysis of Gene Transcription. (A–C) qPCR was performed to determine the fold change in transcription levels of genes involved in the development of amyloid-beta (Aβ+) plaques, neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), and neuronal intracytoplasmic inclusions (NCIs). Top panels: Tissue samples were taken from the parietal lobes (PL, yellow), orbital lobe (OrL, green), and cerebellum (Cer, orange). Bottom panels: Heat maps displaying the relative fold change in gene expression of genes analyzed ranked in order of increasing BMAA exposure. Dolphin IFAW 12-228 Dd was used as a normalization control. BMAA concentrations measured in the PL region is indicated in panel A. Dolphins displayed upregulated gene transcription for all seven genes across all three brain regions. The OrL region showed the most upregulated transcription of genes, especially in genes involved in development of NFTs and NCIs (B). Gene transcription accounted for 24.6% of the total variance in the PL, 41.4% in the OrL and 34.3% in the Cer. Whereas, BMAA exposure accounted for 37.8% of the total variance in the PL, 26.4% in the OrL, and 28.9% in the Cer (p < 0.0001 Two Way ANOVA).