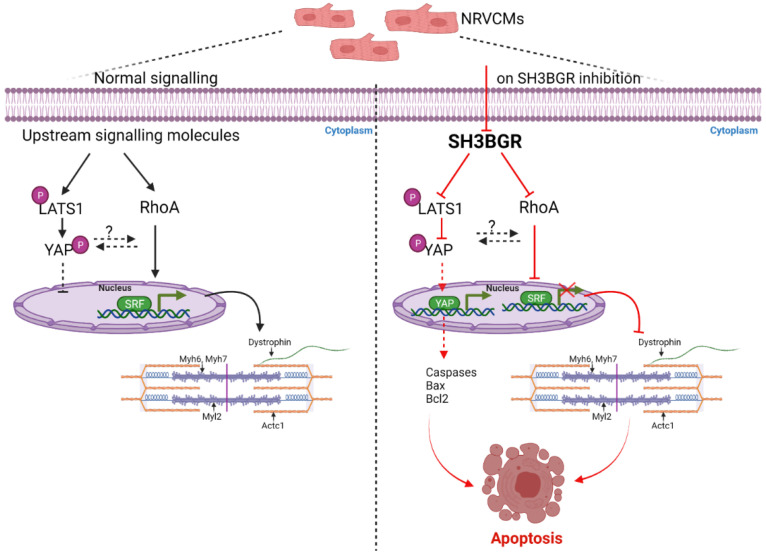
Figure 5.
Mechanistic signaling- As observed in the left side panel, LATS1, when phosphorylated, is retained in the cytoplasm and also retains phosphorylated YAP in the cytoplasm, thereby resulting in no transcriptional activation of YAP. Similarly, RhoA activates SRF; the transcriptional activation of SRF is required for genes involved in sarcomere consisting of myosin heavy chain and light chain, actin, etc. On SH3BGR knockdown, as seen in right panel, phosphorylation of YAP is significantly reduced, thereby activating YAP and resulting in probable activation pro-apoptotic genes. Further, the RhoA–SRF axis is inhibited due to SH3BGR inhibition, resulting in hampered SRF activity, thereby resulting in the sarcomeric instability and leading to apoptosis of NRVCMs. SRF, Serum response factor; Myh6, myosin heavy chain 6; Myh7, myosin heavy chain 7; Myl2, Myosin light chain2; Actc1, Actin Alpha Cardiac Muscle 1; Acta1, Actin Alpha 1skeletal muscle; LATS1, Large tumor suppressor kinase 1; pLATS1, phospho Large tumor suppressor kinase 1; YAP, Yes1 Associated Transcriptional Regulator; pYAP, phospho Yes1 Associated Transcriptional Regulator; Bax, BCL2 Associated X; Apoptosis Regulator; Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma 2.