Figure 5.
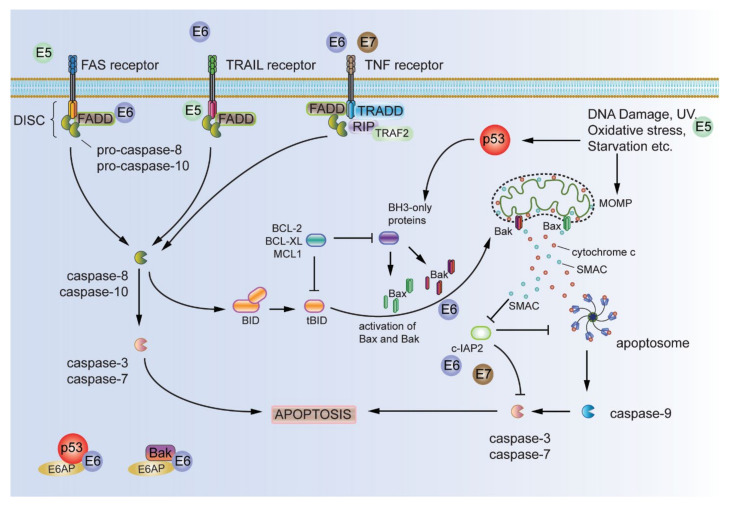
Resisting cell death. One of the major roles played by HPV oncoproteins in resisting cell death is evading apoptosis. Both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways are deregulated to attain this function by HPV-E5, -E6 and -E7. The extrinsic apoptotic pathway is activated upon receptor trimerization and the subsequent recruitment of adaptor molecules and procaspase 8 to the DISC. The activation of caspase 8 then leads to the activation of downstream executioner caspases 3 and 7, leading to cell death/apoptosis. The intrinsic apoptotic pathway is activated by external stimuli (UV-radiation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, starvation, etc.), leading to the formation of pores in the mitochondrial membrane and release of mitochondrial inner membrane proteins (cytochrome c, SMAC) into the cytosol. Released cytochrome c and pro-caspase 9 form the apoptosome, leading to activating caspase 9, which, in turn, activates downstream executioner caspases 3 and 7, leading to apoptosis. E5 can downregulate the Fas receptor and perturb the formation of the DISC complex, thus abrogating the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Further, E5 can perturb ROS-induced Bax activation and inhibit the apoptotic response to UV B radiation. E6 can block extrinsic pathways by binding the death domain, leading to its proteasomal degradation. E6 inactivates p53, Bax and Bak, thus abrogating MOMP and the release of cytochrome c and, thus, inhibiting the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. E6 can also inhibit antiapoptotic c-IAP2, blocking the formation of the apoptosome and activation of the executioner caspases. E7 seems to have a dual function in activating and abrogating apoptosis; however, E7 has been demonstrated to perturb TNF receptor-induced apoptosis by upregulating c-IAP2 and suppressing caspase 8. FADD—Fas-associated protein with death domain, TNF—tumour necrosis factor, TRAIL—FasL and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, TRAF2—TNF receptor-associated factor 2, DISC—death-induced signalling complex, c-IAP2—cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2, RIP—receptor interacting protein and MOMP—mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization.