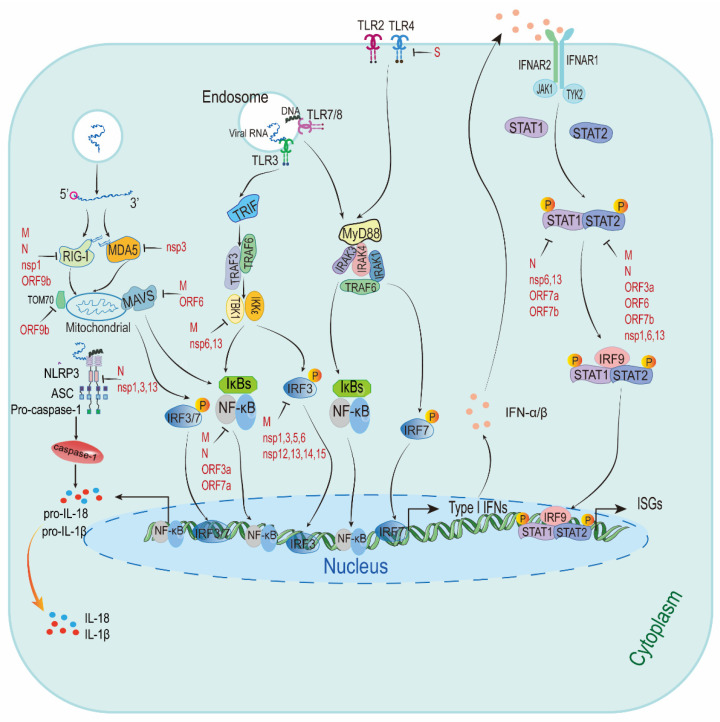
Figure 2.
The predictive model describing the innate immune responses to SARS-CoV-2. There is a simplified figure of the type I IFNs responses after sensing SARS-CoV-2. It has been suggested SARS-CoV-2 escape type I IFNs signaling pathway and ISGs by targeting type I IFNs signaling. Viral proteins with type I IFNs inhibitory activities are highlighted in red. RIG-I: retinoic-acid inducible gene I; MDA5: melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5; MAVS: mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein; nsp1: non-structural protein; TOM70: translocases of outer membrane 70; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3; ASC: apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; pro-IL-18: pro-interleukin (IL)-18; TLR3: Toll-like receptors 3; TRIF: TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β; TRAF3: tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3; TBK1: TANK-binding kinase 1; IKKε: inhibitor of κ-B kinase ε; IκBs: inhibitor κB; NF-κB: nuclear factor κB; IRF3: IFN regulatory factor 3; MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary response 88; IRAK3: interleukin-1-receptor-associated kinase 3; IFNAR1: IFN receptor type I; JAK1: Janus-activated kinase 1; TYK2: tyrosine kinase 2; STAT1: signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; ISGs: interferon-stimulated genes.