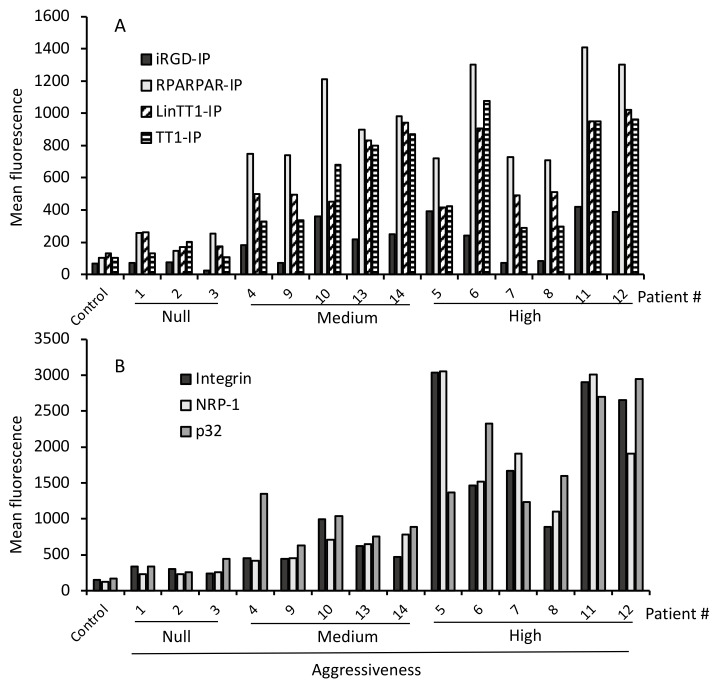
Figure 2.
Selective internalization of TPP-IPs and receptor expression in malignant hepatocytes. (A) TPP-IP internalization. Hepatocytes isolated from benign or malignant liver patient samples were incubated for 4 h with 25 μM of FITC-labeled peptides. The mean fluorescence of internalized peptides was analyzed by flow cytometry and compared to control healthy hepatocytes. Internalization of the TPP-IPs was significantly higher in HCC compared to non-malignant tumors (HCC versus non-malignant tumors or normal hepatocytes respectively, n = 4 to 11 per group, mean ± standard error, iRGD-IP: 61 ± 12 vs. 244 ± 40, p = 0.022; RPARPAR-IP: 191 ± 38 vs. 977 ± 83, p = 0.005; LinTT1-IP: 184 ± 27 vs. 682 ± 73, p = 0.002; TT1-IP: 137 ± 23 vs. 637 ± 93, p = 0.005). (B) Receptor expression. Hepatocytes isolated from non-malignant or tumoral liver samples were incubated with antibodies against NRP-1, p32, and integrin v/b3, followed by an APC-labeled secondary antibody. Samples were analyzed by flow cytometry. Healthy hepatocytes were used as control. Receptor expression levels were significantly higher in tumoral hepatocytes than in non-malignant tumors (HCCs vs. non-malignant tumors or normal hepatocytes, respectively, n = 4 to 11 per group, Integrin v/b3: 254 ± 40 vs. 1416 ± 306, p = 0.005; NRP-1: 211 ± 31 vs. 1410 ± 290, p = 0.005; p32: 303 ± 58 vs. 1530 ± 238, p = 0.01).