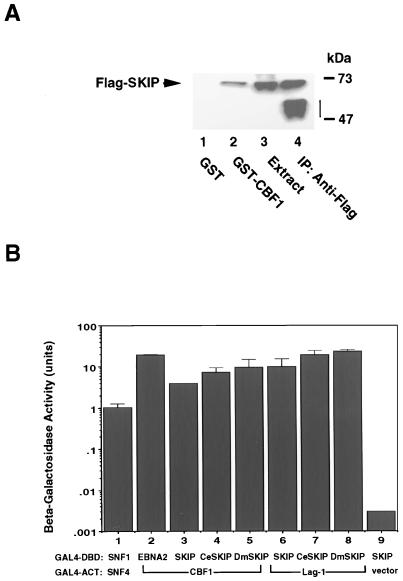
FIG. 2.
SKIP and its homologs interact with CBF1. (A) GST-affinity assay showing binding of Flag-SKIP to GST-CBF1 (lane 2) but not to GST (lane 1). Positive control lanes contained transfected cell extract (10 μl) (lane 3) and Flag-SKIP that was immunoprecipitated (IP) with mouse anti-Flag monoclonal antibody (lane 4). The vertical bar indicates the position of the immunoglobulin heavy chain. (B) SKIP-CBF1 interactions are evolutionarily conserved. Yeast two-hybrid assay in which interaction is measured by induction of beta-galactosidase activity. SNF1-SNF4 (lane 1) and EBNA2-CBF1 (lane 2) formed positive controls, while the SKIP-ACT vector pairing (lane 9) formed the negative control. SKIP, C. elegans SKIP (CeSKIP), and D. melanogaster SKIP (DmSKIP) (lanes 3 to 5) each showed interaction with CBF1. Furthermore the SKIP, C. elegans SKIP, and Drosophila SKIP interactions could also be demonstrated using the C. elegans CBF1 homolog Lag-1 as the interacting partner (lanes 7 to 9). The results shown are averages of results of three experiments, with the standard deviations indicated.