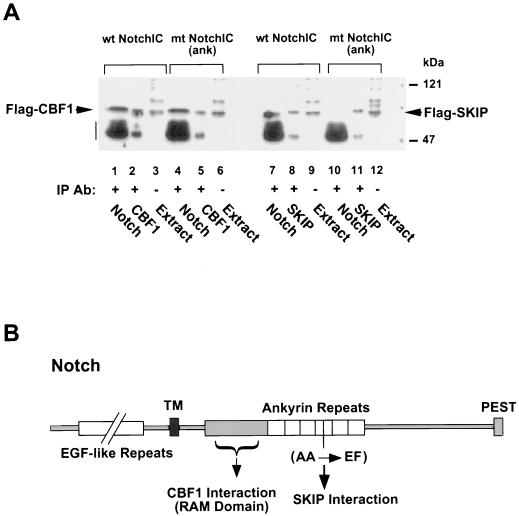
FIG. 9.
Mutation of the fourth ankyrin repeat does not affect NotchIC interaction with CBF1 but abolishes NotchIC SKIP interaction. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation assay using extracts of cells cotransfected with the wild-type (wt) or ankyrin repeat mutant NotchIC [mt NotchIC(ank)] and either Flag-CBF1 or Flag-SKIP. Western blots of the immunoprecipitated proteins were probed with mouse anti-Flag monoclonal antibody to detect Flag-CBF1 (lanes 1 to 6) or Flag-SKIP (lanes 7 to 12). Flag-CBF1 coprecipitated with both wild-type and mutant NotchIC (lanes 1 and 4), whereas Flag-SKIP coprecipitated with wild-type but not mutant NotchIC (lanes 7 and 10, respectively). Lane 1, coprecipitation with anti-Notch rabbit antibody; lane 2, direct precipitation with anti-CBF1 rabbit antibody; lane 3, transfected cell extract (10 μl); lane 4, coprecipitation with anti-Notch rabbit antibody; lane 5, direct precipitation with anti-CBF1 rabbit antibody; lane 6, transfected cell extract (10 μl); lane 7, coprecipitation with anti-Notch rabbit antibody; lane 8, direct precipitation with anti-SKIP rabbit antibody; lane 9, transfected cell extract (10 μl); lane 10, coprecipitation with anti-Notch rabbit antibody; lane 11, direct precipitation with anti-SKIP rabbit antibody; lane 12, transfected cell extract (10 μl). The amount of extract used for direct precipitations was one-quarter of that used for coprecipitations. The vertical bar indicates the position of the immunoglobulin heavy chain. IP, immunoprecipitation; Ab, antibody. (B) Schematic of the Notch protein showing the relative locations of the CBF1 and SKIP binding domains and the location of the ankyrin repeat mutation. TM, transmembrane domain. EGF, epidermal growth factor; PEST, protein turnover motif.