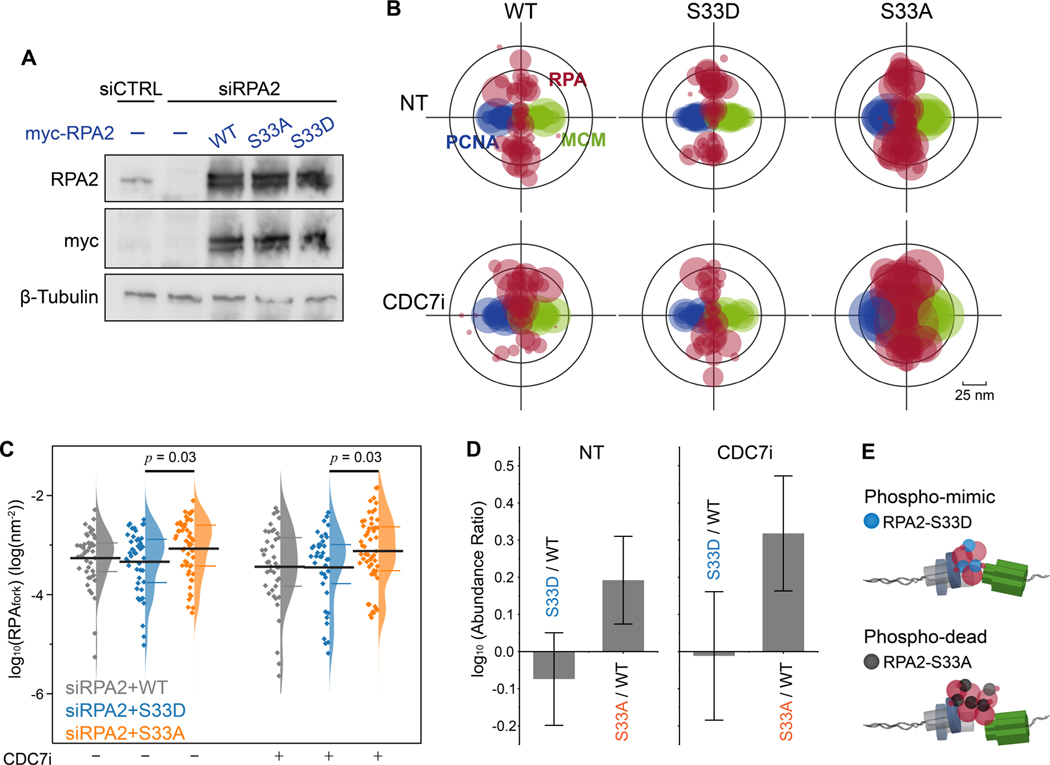
Figure 4. ATR regulates the accumulation of RPA at forks via phosphorylation of RPA2 Ser-33.
(A) Western-blot analysis of the expression of RPA2 and RPA2 mutants for RPA2 siRNA and RPA2 siRNA + transfection of myc-tagged wild-type (WT) RPA and S33A, S33D RPA2 mutants.
(B) Overlaid PCNA-RPA-MCM TCF-resolved single-replisome configurations from SMLM images of single cells harboring RPA2 WT and RPA2 phosphor-mutants and under CDC7i treatment conditions. Circle size represents the average density of RPA at each fork within a nucleus.
(C) Quantification of the levels of RPAfork for the TCF-resolved single replisome configurations shown in (B) reveals that the expression of the phosphor-dead RPA2 S33A results in an accumulation of RPA at forks that is independent of origin firing. Mean values and the 1st and 3rd quartile were marked as black and colored bars, respectively, N = 43, 48, 52, 41, 39, and 56 for WT-CDC7i-, S33D-CDC7i-, S33A-CDC7i-, WT-CDC7i+, S33D-CDC7i+, and S33A-CDC7i+, respectively.
(D) Quantification of the abundance ratio between data as indicated. Error bars in log (Abundance Ratio) is the propagated SEM.
(E) Schematic illustration of the regulation of RPAfork levels by ATR via phosphorylation of RPA2 at Ser33.