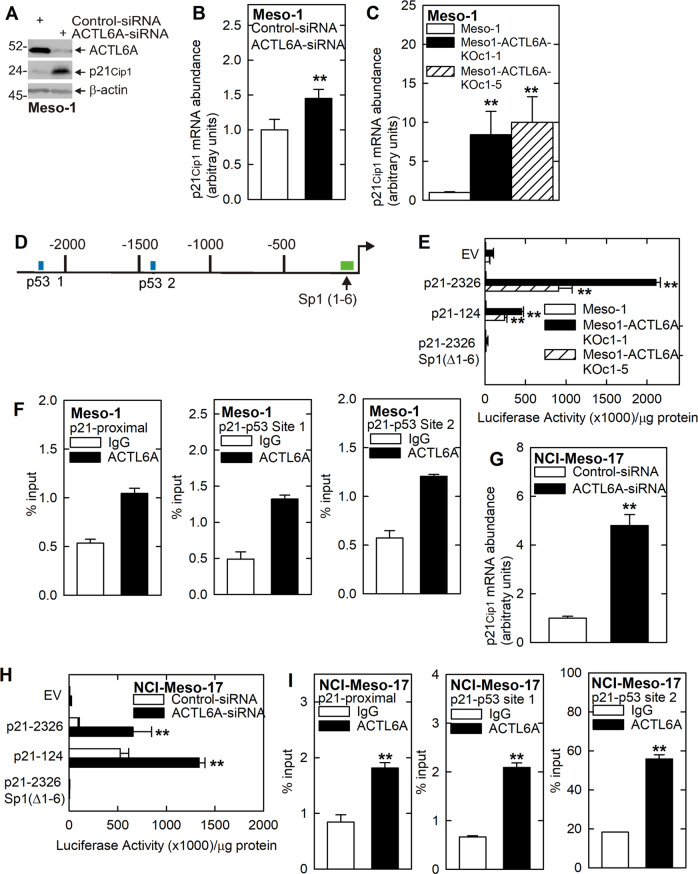
Fig. 4. ACTL6A suppresses p21Cip gene transcription to maintain the mesothelioma cancer phenotype.
A, B ACTL6A knockdown increases Meso-1 cell p21Cip1 mRNA expression and protein level. C ACTL6A knockout Meso-1 cells express increased p21Cip1 mRNA. D Map of the full-length p21Cip1 promoter showing the p53-1 and p53-2 sites in the distal promoter and six Sp1 site in the proximal promoter. The top sequence indicates the authentic p53 site sequences. Our previous report indicates the mutations that inactivate these sites [28]. E ACTL6A knockout Meso-1 cells display enhanced p21Cip1 promoter activity for the full-length (p21-2326) and proximal (p21-124) promoter, and mutation of the six Sp1 sites eliminates the response. F Chromatin IP, using Meso-1 extracts, shows ACTL6A binding to the p21Cip1 promoter p53 binding sites and the proximal promoter Sp1 sites. G–I ACTL6A knockdown in NCI-Meso-17 cells increases p21Cip1 mRNA level and p21Cip1 promoter activity and this is associated with ATL6A binding to the p21Cip1 promoter p53 and Sp1 sites. As observed for Meso-1 cells, mutation of the proximal Sp1 sites eliminates transcriptional activity. Double asterisks indicate a significant increase (n = 3, p ≤ 0.001).