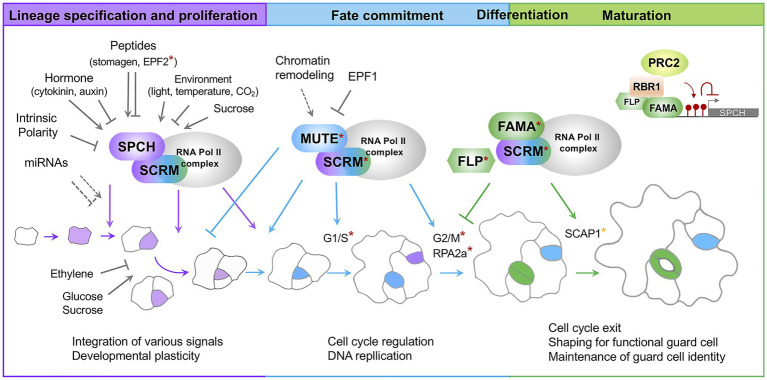
Figure 1.
A current model for Stomatal development in Arabidopsis. Stomatal lineage progression is mediated by a sequential action of the developmental stage-specific transcription factors. SPCH/SCRM are responsible for lineage specification and proliferation; MUTE/SCRM for fate commitment; FAMA/SCRM for differentiation and maturation. Developmental and environmental signals primarily modulate the first step mediated by SPCH/SCRM. A subunit of the RNA polymerase II complex and associated proteins interact with core transcription factors. Direct targets for MUTE and FAMA are denoted by asterisks in red and orange, respectively. Cells highlighted in purple indicate stomatal lineage precursors. Cells highlighted in blue are late meristemoids and GMCs. Cells highlighted in green are immature and mature guard cells. Colored arrows indicate positive regulation of transcription factors. Colored, inverted Ts indicate negative regulation of transcription factors. Arrows and closed lines in gray indicate developmental and environmental factors regulating transcription factors or stomatal lineage cells. A dotted line indicates potential regulation. SPCH, SPEECHLESS; SCRM, ICE1/SCRM2; FLP, FOUR LIPS; RPA2A, a core subunit of Replication Protein A complexes; SCAP1, STOMATAL CARPENTER 1; RBR1, RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED 1; PRC2, Polycomb Repressive Complex 2; EPF, Epidermal Patterning Factor; G1/S G2M, phases of cell cycle.