FIGURE 5.
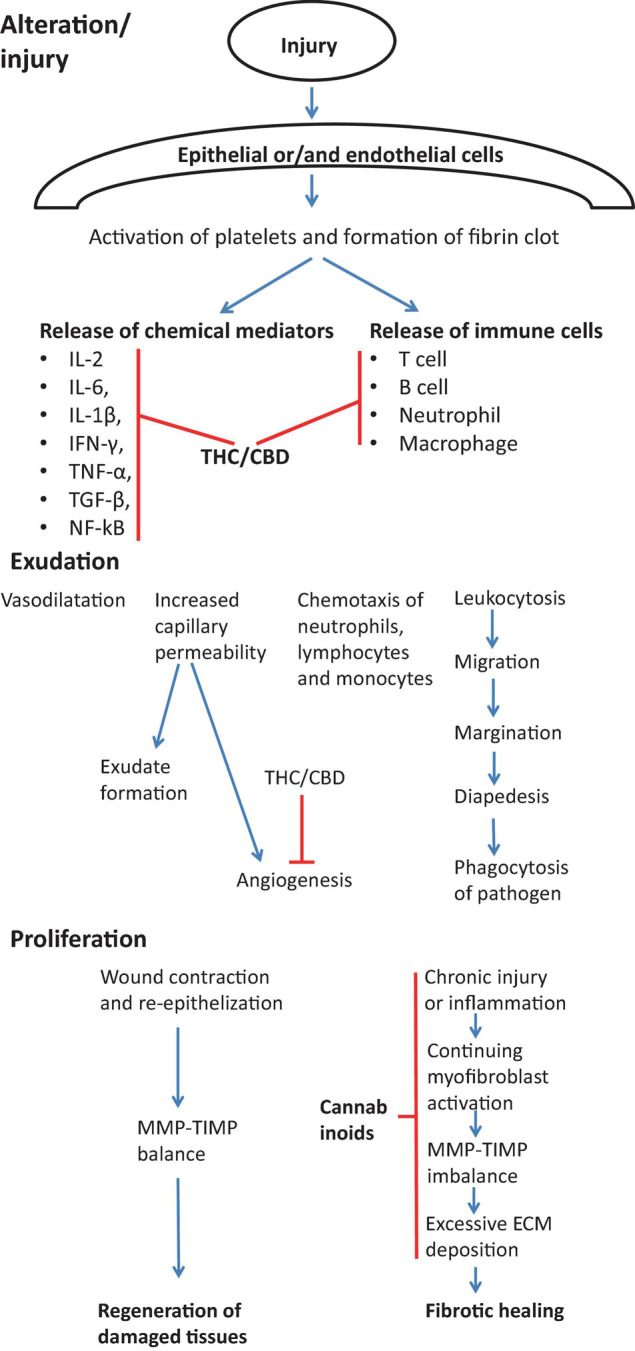
Effect of cannabinoids on various stages of wound healing in view of preventing/treating fibrosis. During the first stage of wound healing cannabinoids are responsible for inhibiting immune response by suppressing the release of immune cells into the injury cite and by inhibiting Th1 response and main pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, IL-1β, IFN-γ, TNF-α, TGF-β, NF-kB) (Watzl et al., 1991; Srivastava et al., 1998; Dinu et al., 2020). During exudation stage, cannabinoids inhibit the angiogenesis (Wietecha and DiPietro, 2013). Cannabinoids also actively contribute to the proliferation stage by suppressing chronic inflammation (Costa et al., 2007; Gallily et al., 2018), myofibroblast activation (Garcia-Gonzalez et al., 2009), the excessive deposition of ECM components (Garcia-Gonzalez et al., 2009) and normalization of TIMP-MMP imbalance (Garcia-Gonzalez et al., 2009).
