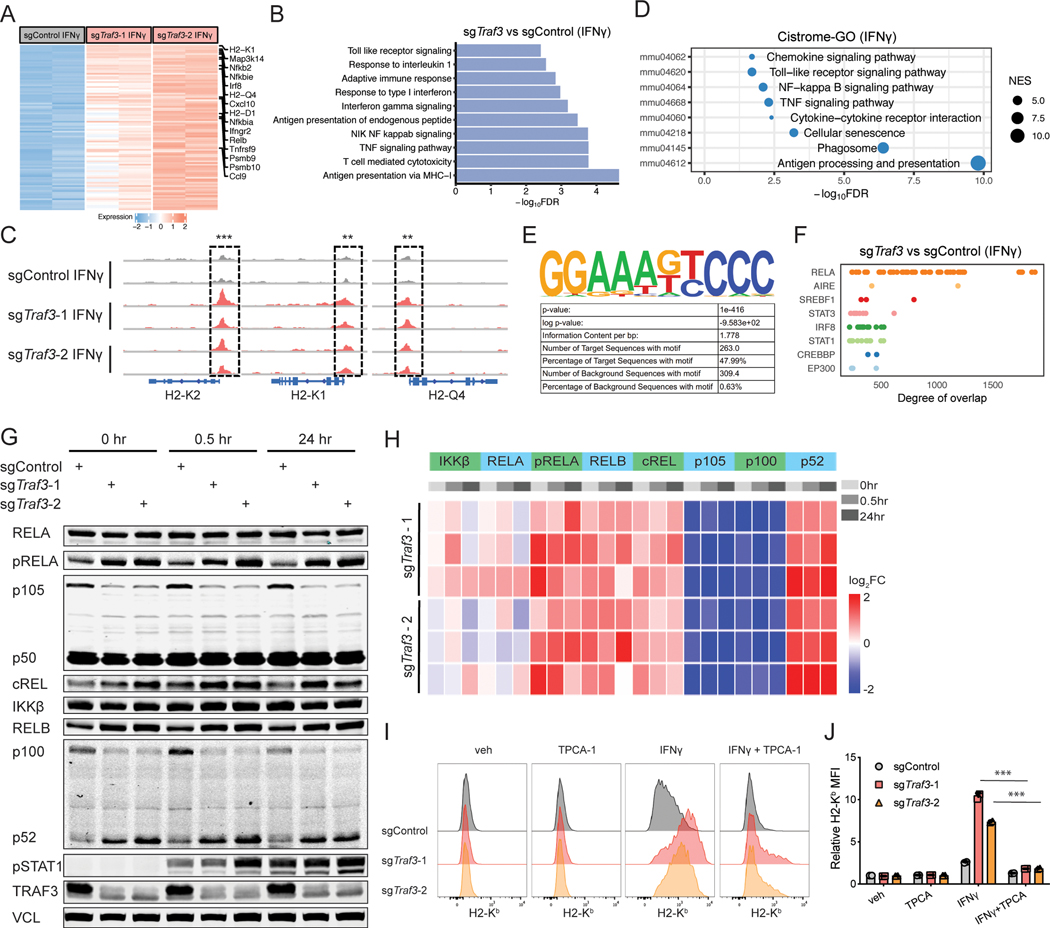
Figure 2. TRAF3 deficiency upregulates MHC-I through NF-κB.
(A) RNA-seq of B16F10 cells transduced with sgControl or sgTraf3 shows upregulation of MHC-I-related genes in the absence of Traf3. Heatmap of differential expression of genes induced by TRAF3 deficiency with IFNγ treatment. (B) GSEA enrichment analysis of upregulated pathways (GO biological pathway) in sgTraf3 cells compared to sgControl cells with IFNγ treatment. Multiple pathways, such as antigen presentation and NF-kB signaling, were upregulated by the deletion of Traf3. (C) ATAC-seq of Traf3-normal or -deficient B16F10 cells revealed that TRAF3 deficiency leads to higher chromatin accessibility near genes encoding components of the MHC-I complex. (D) Cistrome-GO analysis of the more accessible regions in sgTraf3 compared to sgControl cells with IFNγ treatment. (E) Cistrome toolkit analysis of ATAC-seq data revealed that DNA-binding sites of RELA were more open in the Traf3-deficient cells. (F) Enrichment of motifs in the accessible chromatin regions specific to Traf3-deficient cells. The top enriched motifs (RELA) is shown. (G) Typical immunoblot of NF-κB signaling components in Traf3-normal or -deficient B16F10 cells in response to IFNγ induction. B16F10 cells transduced with sgControl or sgTraf3 were induced by 1ng/ml IFNγ for 0, 0.5, or 24 hours, and then harvested for immunoblot. Data from 1 typical experiment out of 3 biological replicates is shown. (H) Quantification of immunoblot signals from panel (G) based with 3 biological replicates. TRAF3 deletion leads to upregulated NF-kB signaling. (I-J) B16F10 cells transduced with control sgRNA or sgTraf3 were treated with vehicle control, IFNγ (1ng/ml), and/or TPCA-1 (1μM) for 48 hours, and then assessed on their MHC-I and PD-L1 levels. (I) Typical histogram of H2-Kb and PD-L1 FACS plot of control or Traf3-deficient B16F10 cells in each treatment condition. (J) Quantification of MFI of H2-Kb or PD-L1 from (I). Values are normalized to sgControl group with vehicle treatment. (***P < 0.001; Two-way ANOVA with Benjamini-Hochberg post test comparing IFNγ and IFNγ+TPCA groups).