Figure 1. Exposure to BALF from ARDS patients and healthy controls are non-toxic to hMSCs.
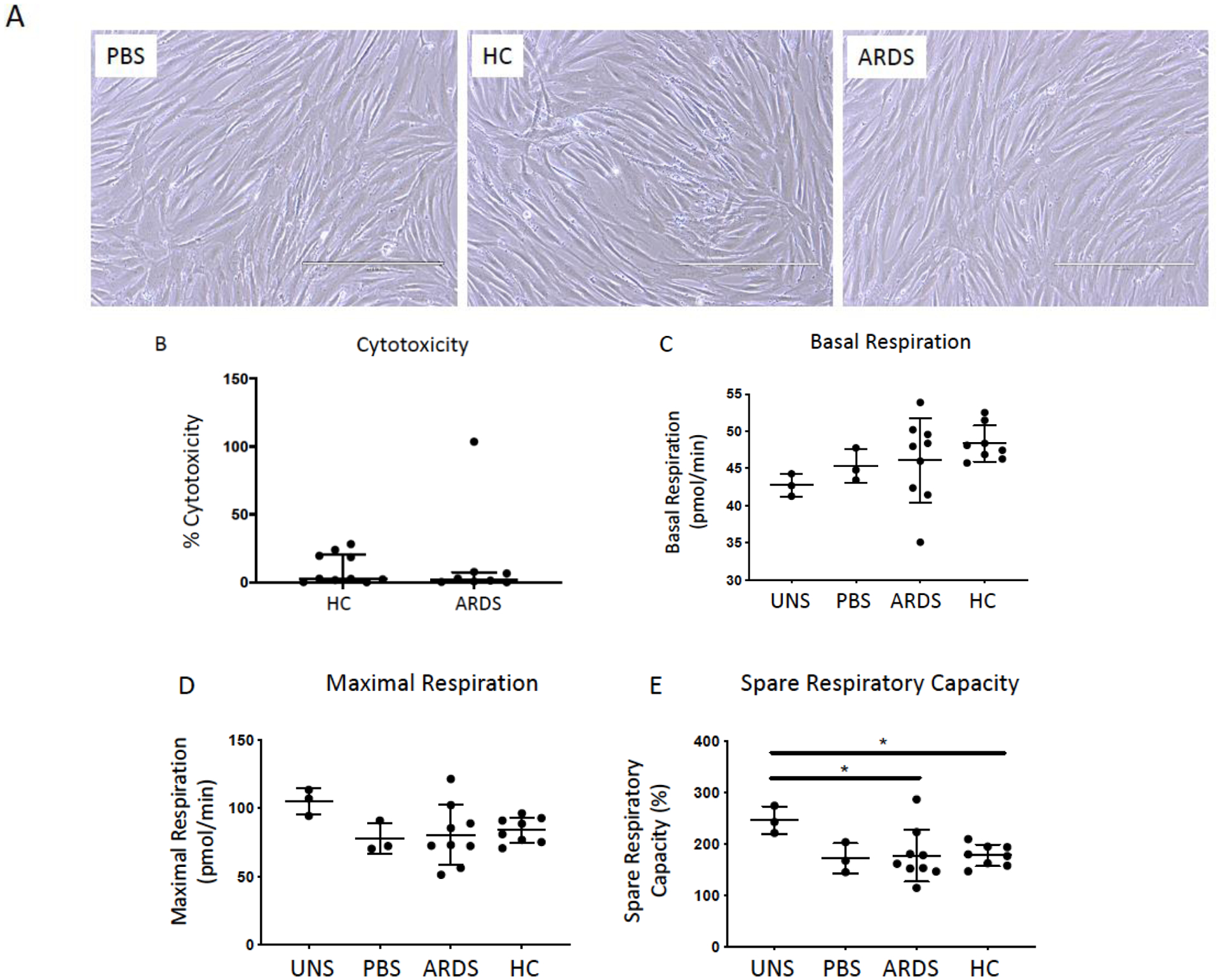
Representative phase contrast photomicrographs (10X) of hMSCs exposed for 24 hours to 20% BALF samples obtained from ARDS patients or from healthy control subjects (HC). PBS-exposed (20%) hMSCs were used as controls. Scale bar represents 400μm and photomicrographs have been brightness/contrast adjusted (A). Cytotoxicity was evaluated in conditioned medium utilizing a standard LDH assay following 24 hours exposure (ARDS: n= 8 and HC: n=10). Data are presented as median with interquartile range of % cytotoxicity (B). To assess the impact of ARDS (n=9) and healthy control BALF (n=8) samples on hMSC mitochondrial function, basal respiration (C), maximal respiration (D), and spare respiration capacity (E) was measured in hMSCs pre-exposed (24 hours) utilizing XF-96e Extracellular Flux Analyzer and compared to PBS-exposed (n=3) and unstimulated (serum free media only, n=3). Data are presented as means ± with SD and statistical analysis was performed by Shapiro-Wilk test, followed by a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test. Abbreviations: HC, healthy control; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; uns, unstimulated (serum free media only); *, p≤0.05.
