Figure 2. ARDS BALF as well as healthy control BALF exposure activates hMSCs to release a spectrum of mostly pro- but some anti-inflammatory mediators.
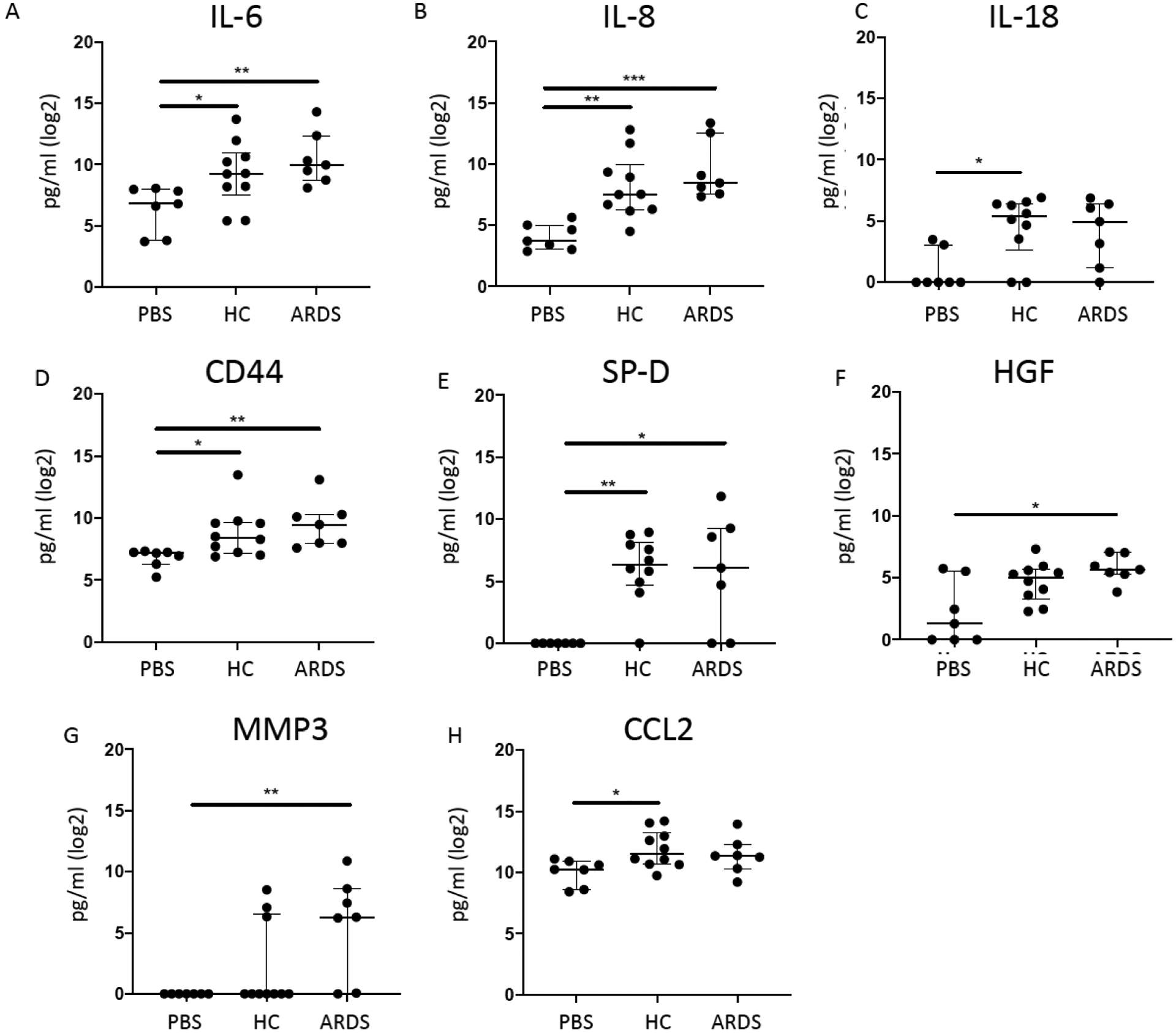
To assess if the secretome profiles of hMSCs exposed to ARDS BALF (n=7) samples differed from healthy control BALF-exposed hMSCs (n=10) and PBS-exposed hMSCs (n=7), conditioned media after BALF or PBS exposure was assessed for a range of inflammatory and other mediators including IL-6 (A), IL-8 (B), IL-18 (C), CD44 (D), SP-D (E), HGF (F), MMP3 (G), and CCL2 (H). Data are presented as median with interquartile range of log2 normalized values, and statistical analysis was performed by Shapiro-Wilk test, followed by Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s post hoc test by comparing to the unstimulated control group. Abbreviations: HC, healthy control; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; IL-6, Interleukin 6; IL-8, Interleukin 8; IL-18, Interleukin 18; CD44, CD44 Molecule/Hyaluronate Receptor; SP-D, Surfactant protein D; HGF, Hepatocyte growth factor; MMP3, matrix metalloproteinase-3; CCL2, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2/ monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; *, p≤0.05; **, p≤0.01. 0.01.
