Fig. 1. The Legionella effector MavQ is an atypical PI 3-kinase.
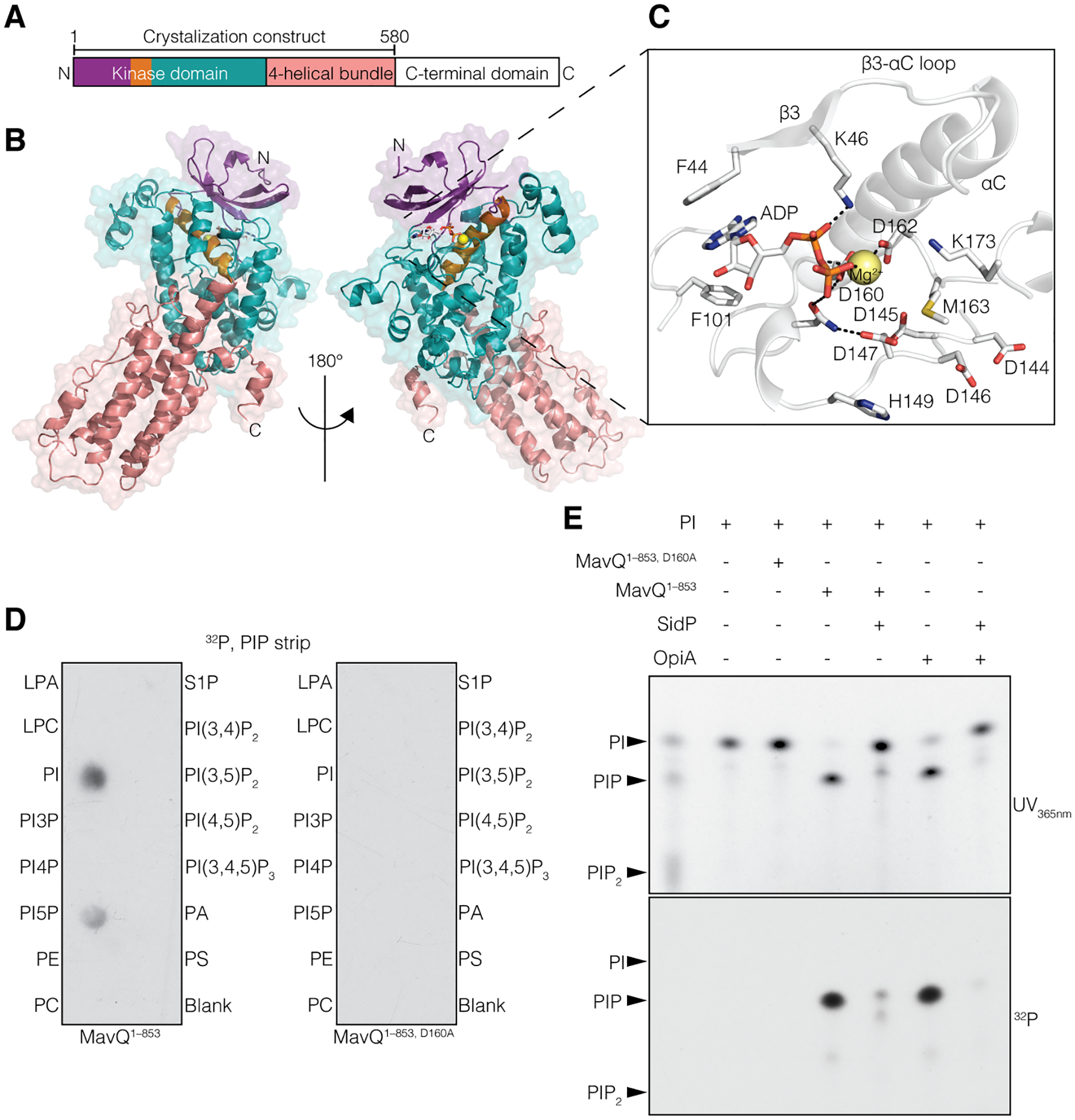
(A and B) Domain architecture of MavQ (A) and overall structure of MavQ1–580 (B) depicting the N-lobe (violet), the αC-helix (orange), the C-lobe (teal), the four-helical bundle (4HB; salmon) and the C-terminal domain (CTD; white). (C) Magnified view of MavQ1–580 kinase active site depicting the interactions (dashed lines) involved in nucleotide binding. The ADP is shown as sticks and the Mg2+ ion as a yellow sphere. (D) Autoradiograph depicting the transfer of γ−32P from [γ−32P]ATP onto PI and PI5P on a PIP strip by MavQ1–853 but not the predicted catalytically inactive mutant MavQ1–853, D160A. (E) Chromatogram depicting the incorporation of γ−32P from [γ−32P]ATP by MavQ1–853 or the inactive mutant using BODIPY-labeled PI as a substrate. Reactions were subsequently treated with or without the PI 3-phosphatase SidP. OpiA, a Francisella tularenesis PI 3-kinase (5), was used as a positive control. Reaction products were separated by thin layer chromatography and visualized by UV365nm fluorescence and autoradiography.
