Figure 1. Identification of Dynarrestin.
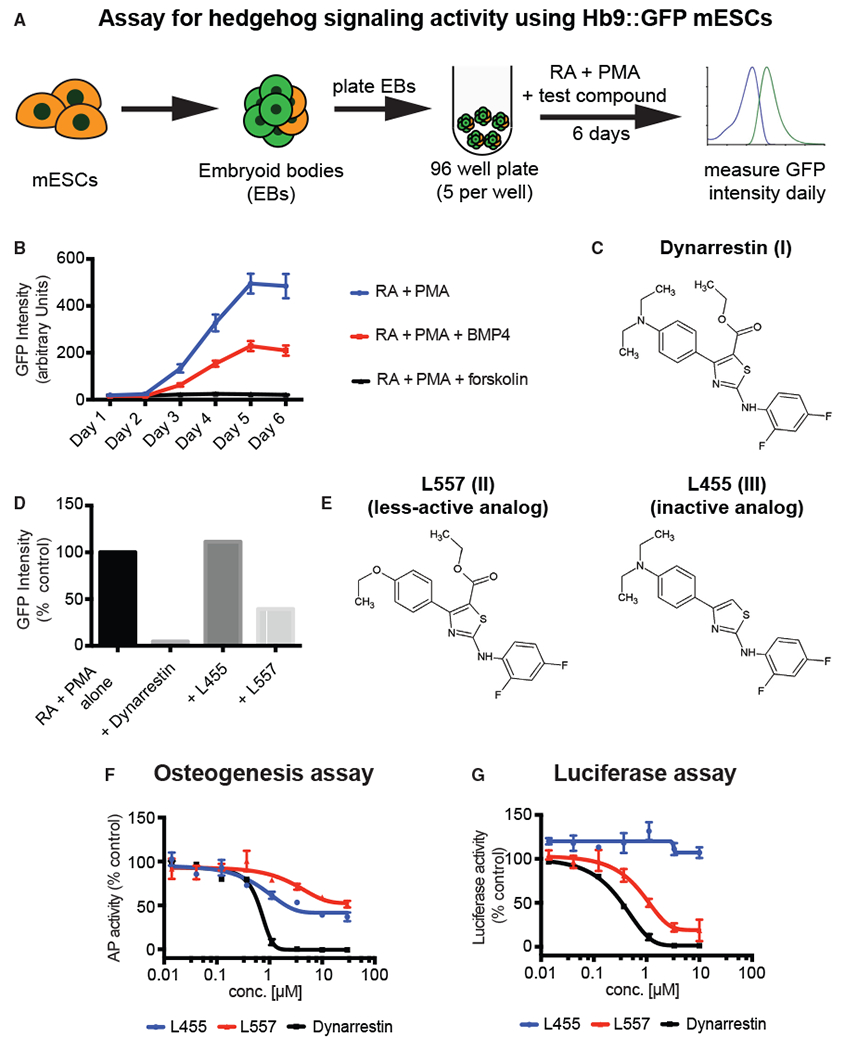
(A) Schematic of the assay for embryoid body (EB)-based differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) into motor neurons in an Hh-dependent manner.
(B) Time course of Hb9:GFP expression under the indicated conditions.
(C) Chemical structure of dynarrestin.
(D) Effect of the indicated compound on Hb9:GFP intensity in treated EBs (Day 5).
(E–G) Chemical structure of dynarrestin analogs (E). Effects of the indicated compounds in assays of (F) Hh-dependent osteogenesis of C3H10T1/2 cells and (G) luciferase activity using Shh-LIGHT2 cells.
Error bars indicate data range. See also Figures S1 and S2.
