Figure 5.
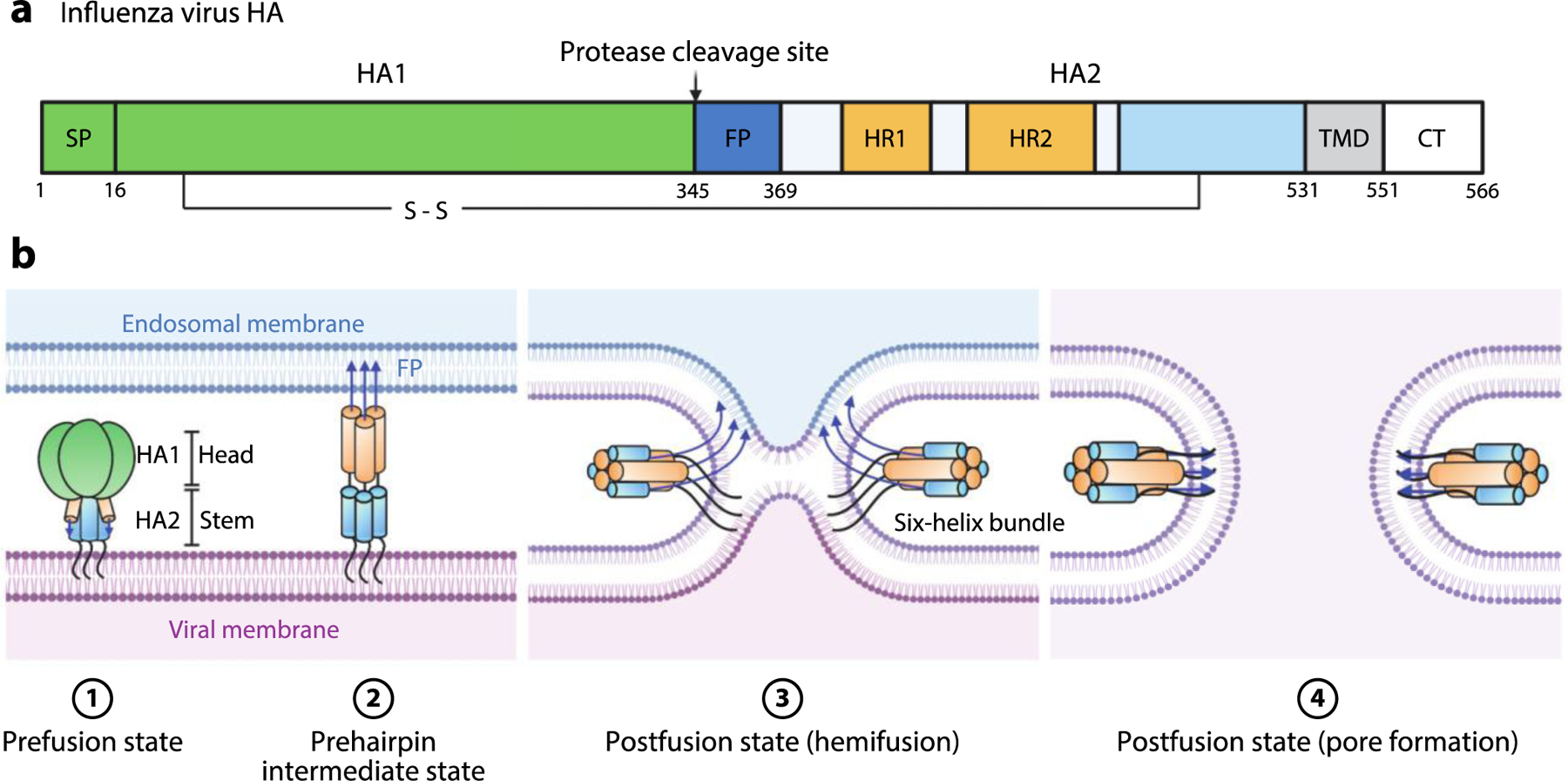
Influenza virus HA-mediated membrane fusion. (a) Schematic diagram of HA. The positions of the SP, HA1, protease cleavage site, HA2, FP, HR1, HR2, disulfide bond, TMD, and CT are shown. (b) Schematic of the fusion process. Viral entry is initiated by binding of HA1 to sialic acid moieties on the plasma membrane. The virion is internalized by endocytosis. The pH of the late endosome is the physiological trigger for extension of the HA2 FP toward the endosomal membrane to produce the extended, prehairpin intermediate. This is followed by refolding of HA2 monomers around the HA1 inner core. Formation of this six-helix bundle drives the viral TMD and FP into proximity, along with the viral and endosomal membranes, thereby facilitating hemifusion and subsequent pore formation upon full fusion of the two membranes. Abbreviations: CT, cytoplasmic tail; FP, fusion peptide; HA, hemagglutinin; HR, heptad repeat; SP, signal peptide; TMD, transmembrane domain. Figure adapted from images created with BioRender.com.
