Figure. 8.
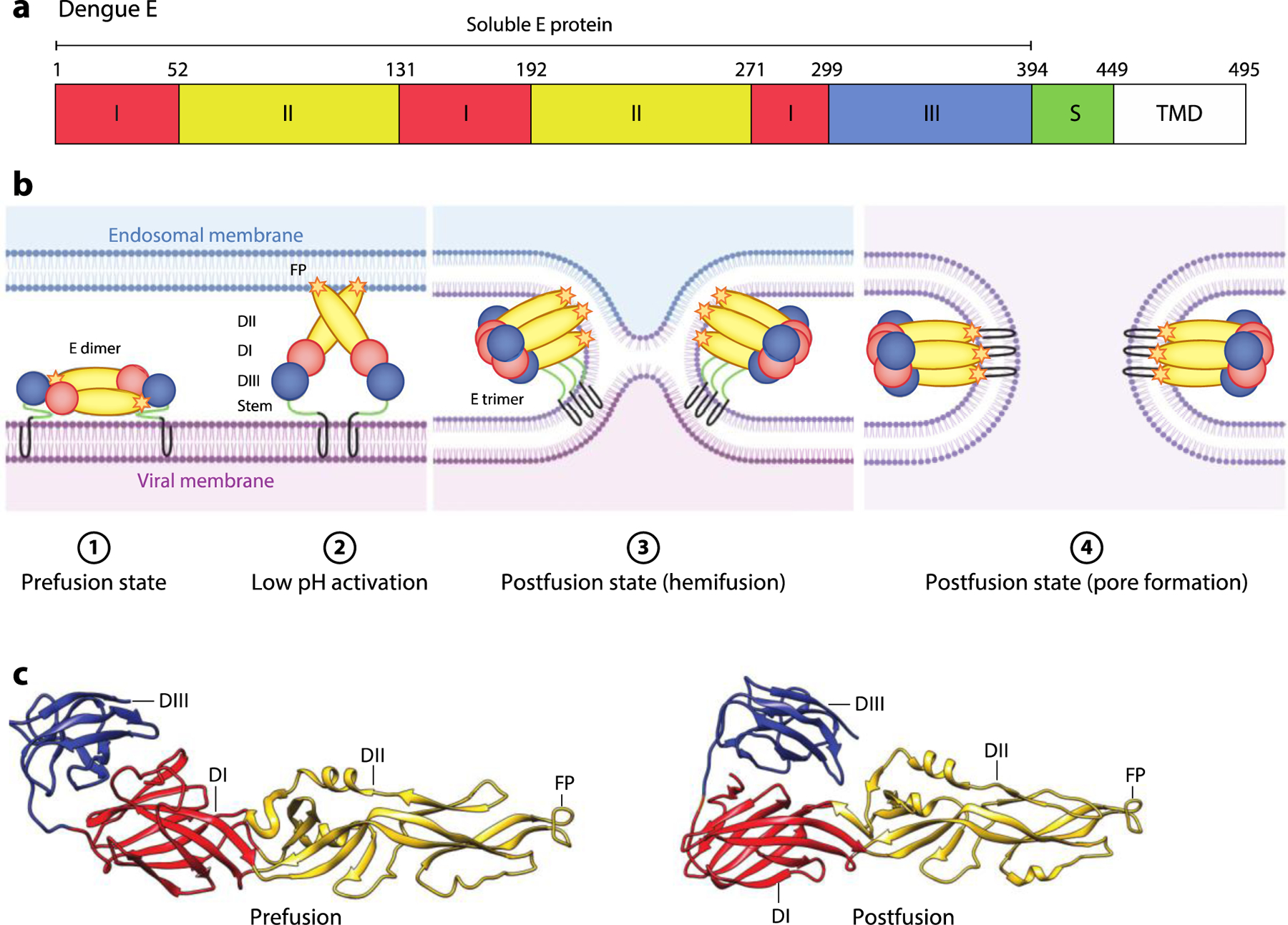
Flavivirus E-mediated membrane fusion. (a) Schematic diagram of dengue E. The locations of DI, DII, DIII, stem region S region, TMD, and soluble E protein (residues 1–394) are shown. (b) Schematic of the E-mediated fusion process. In the prefusion state, the mature E dimer is anchored on the viral membrane. Exposure to low pH in the endosome triggers dissociation of the E dimer and extension of the FP toward the endosomal membrane. Rearrangement of E as a trimeric species is followed by movement of DIII toward DI. Zipping up of this extended intermediate through new interactions of the S region with DII pulls the viral TMD and FP into proximity, and with them, the viral and endosomal membranes. This facilitates hemifusion and subsequent formation of a fusion pore. (c) Pre- (PDB:1OAN) and postfusion (PDB:1OK8) structures of dengue E protein. The DI, DII, DIII, and FP are indicated. Abbreviations: D, domain; FP, fusion peptide; S, stem; TMD, transmembrane domain. Figure adapted from images created with BioRender.com.
