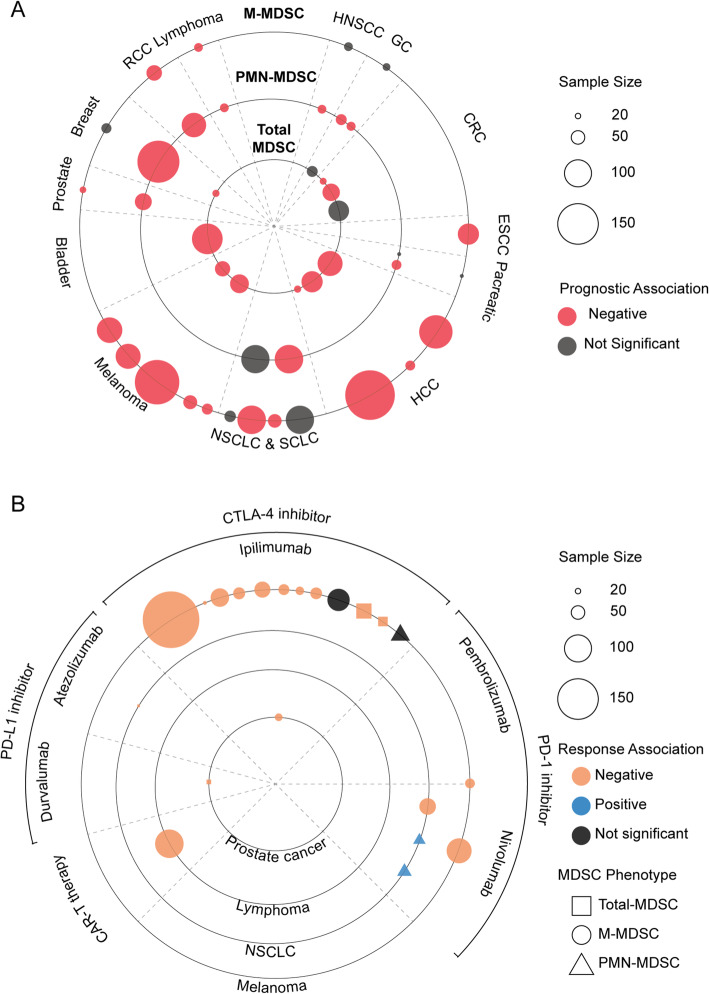
Fig. 5.
MDSC as a prognostic factor of tumor treatment. A: Data from studies (Supplementary Table 1) involving patients across cancer types displayed were analyzed regarding the relevance of MDSC and the prognoses of cancer patients receiving anti-tumor therapy. Each circle represents a study and the size of the circle is proportional to the number of the patients involved. The association of the MDSC level and the prognoses of cancer patients is demonstrated as red (negative correlation) or grey (no significant correlation); B: Data from studies (Supplementary Table 2) involving patients across cancer types displayed were analyzed regarding the relevance of MDSC and the response of cancer patients receiving immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Square represents total MDSC, circle represents M-MDSC, and triangle represents PMN-MDSC. Each square/circle/triangle represents a study and the size is proportional to the number of the patients involved. The association of the MDSC level and the response of ICI treatment is demonstrated as orange (negative correlation), blue (positive correlation), and deep grey (no significant correlation). Abbreviations: MDSC, Myeloid-derived suppressor cell; M-MDSC, Monocytic MDSC; PMN-MDSC, Polymorphonuclear MDSC; HNSCC, Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; GC, Gastric carcinoma; CRC, Colorectal cancer; ESCC, Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; HCC, Hepatocellular carcinoma; NSCLC, Non-small cell lung cancer; SCLC, Small cell lung cancer; RCC, Renal cell carcinoma