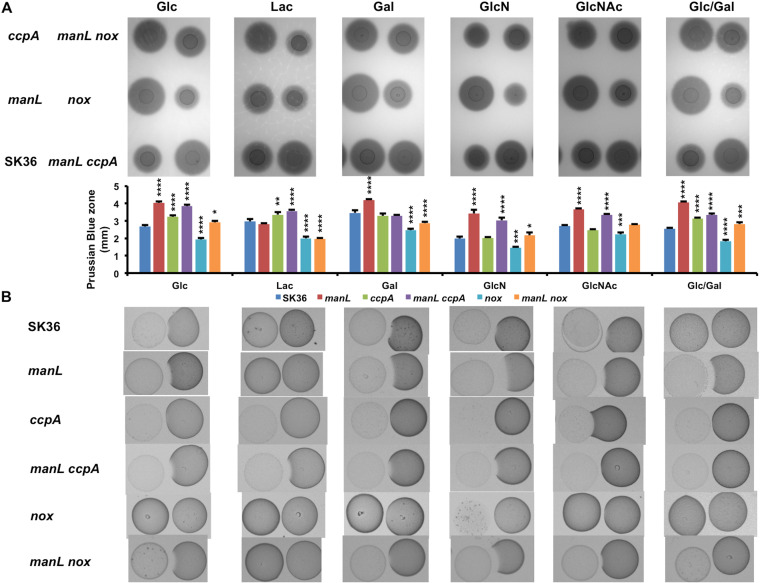
FIG 4.
H2O2 production (A) and antagonism of S. mutans (B) on plates. Cultures of SK36, the wild type (MMZ1896), and its mutant derivatives deficient in manL, ccpA, manL ccpA, nox, and manL nox were each dropped onto the surface of TY-agar plates prepared with 20 mM glucose, lactose, galactose (Gal), GlcN, GlcNAc, or 10 mM (each) glucose and galactose (Glc/Gal) and were incubated for 24 h in an aerobic environment (with 5% CO2). (A) For direct measurement of H2O2 release, the plates contained 0.1% each of FeCl3·6H2O and potassium hexacyanoferrate(III), which formed a Prussian blue zone upon reacting with H2O2. All images were photographed under the same settings, with the zones of Prussian blue measured using VisionWorks software. Each sample was assayed at least three times. Asterisks represent statistical significance relative to the wild type in each group, assessed by a one-way ANOVA test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001). (B) For antagonism of S. mutans, the same amount of UA159 culture was placed to the right of the first colony, followed by another 24 h of incubation. Each antagonism experiment was repeated three times using biological replicates, with a representative result being presented.