FIGURE 1: LXR/RXR activation suppresses IL-23/IL-17 mediated gingival inflammation and alveolar bone loss:
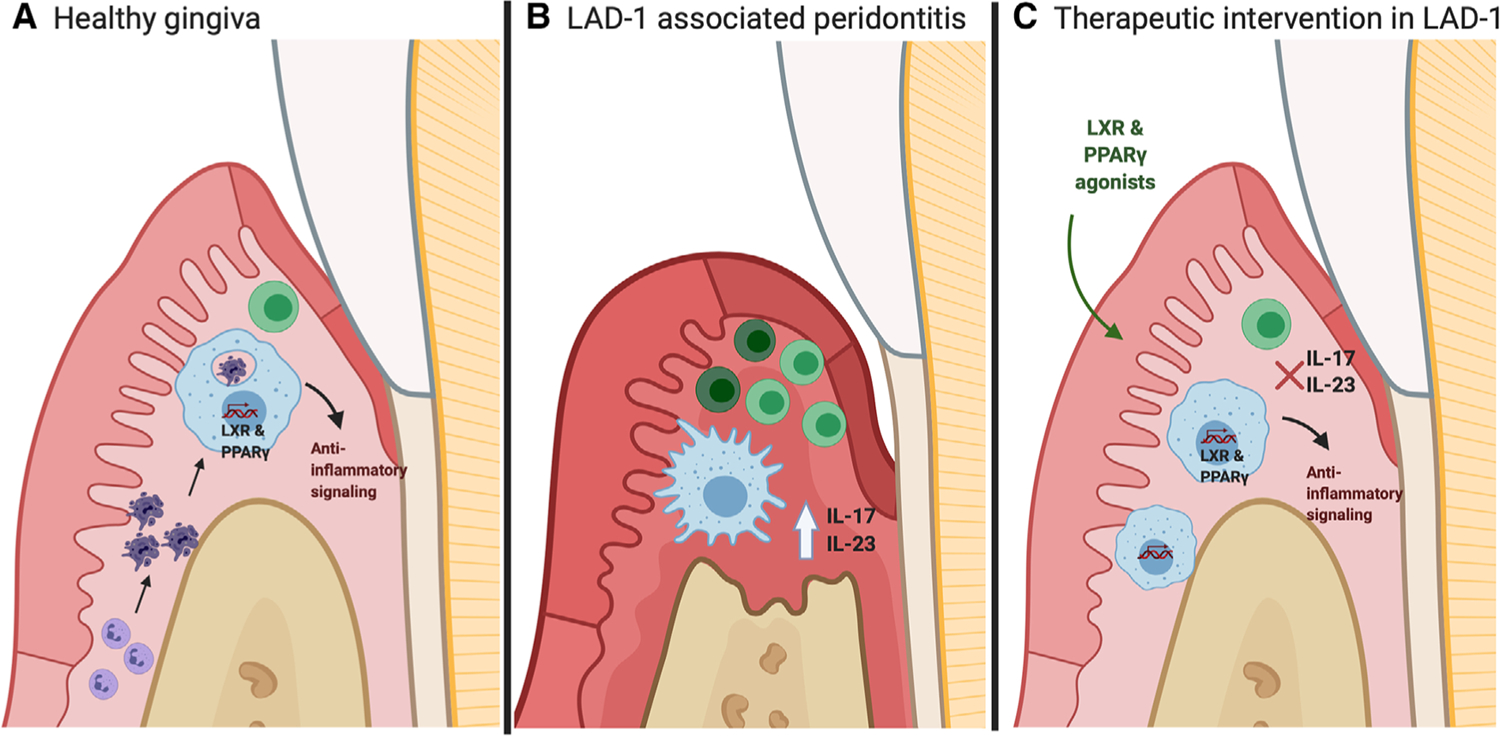
(A) Efferocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils by tissue Mϕs/dendritic cells activates LXR/RXR dependent anti-inflammatory mediators, suppressing IL-23 levels in the gingiva. (B) Genetic deletion of CD18 results in dramatic loss of neutrophil transmigration into gingival tissues, disrupting efferocytosis induced feedback inhibition of the IL-23/IL-17 axis. (C) Intra-gingival administration of LXR and PPAR agonists induces the expression of LXR/RXR dependent genes, consequently suppressing IL-23/IL-17 mediated alveolar bone loss and gingival inflammation
