Figure 1.
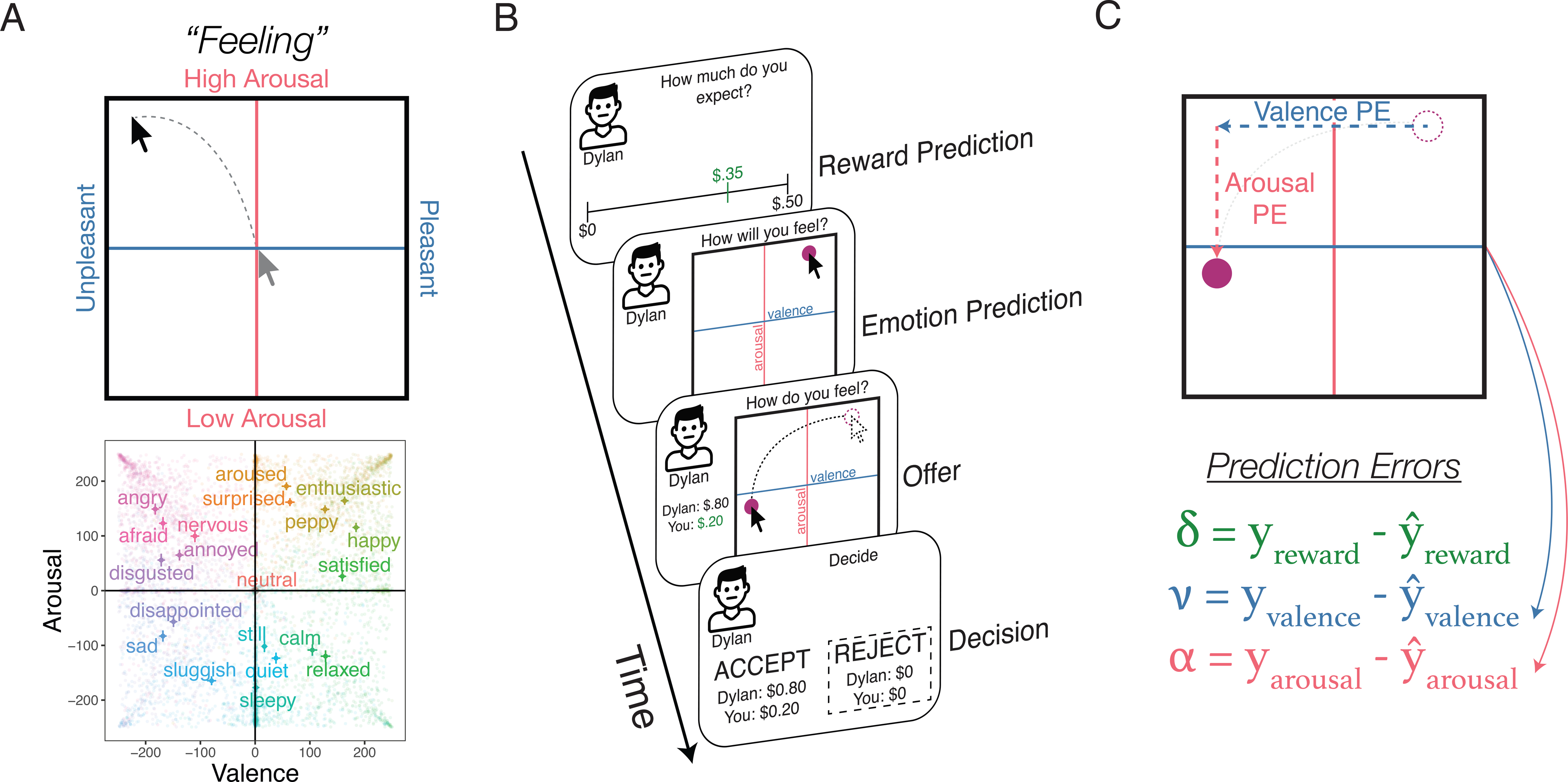
A) Emotion Classification Task. Participants rate a series of 20 feelings on the dynamic Affective Representation Mapping (dARM) measure. The dARM is a 500 × 500 pixel grid, which is only delineated by a horizontal (valence axis) and vertical line (arousal axis) along with their labels. The graph below the grid shows the average ratings for 20 feeling words all participants rated in Experiment 1 (each semi-transparent datapoint reflects one individual rating). Error bars reflect 95% confidence intervals. B) Ultimatum Game Trial Design. Here, we show how the dARM is used in conjunction with the Ultimatum Game to capture emotion expectations and experiences. On each trial, participants make a prediction about how much money they expect to be offered, as well as a prediction about the emotions they expect to experience. Upon seeing the actual offer, participants report their current emotional experience. Finally, participants decide to either accept or reject the offer. C) Calculating Reward and Emotion Prediction Errors. We calculate three trial-level empirical prediction errors: a reward prediction error (δ), a valence prediction error (ν), and an arousal prediction error (α). In the equations, refers to an individual’s prediction about the reward or emotion they would experience, and y refers to their actual experience.
