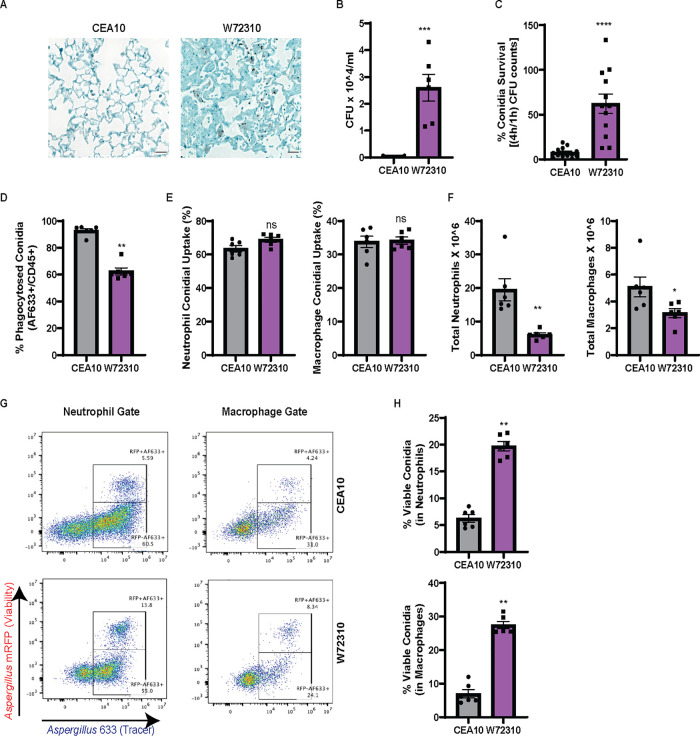
FIG 1.
A. fumigatus clinical isolate W72310 persists longer in the murine lung and is resistant to leukocyte-mediated death compared to the common laboratory strain CEA10. (A) C57BL/6 mice were intranasally inoculated with 1 × 10^7 live CEA10 or W72310 conidia and euthanized after 7 days. Lungs were fixed in formalin and stained for fungi (GMS stain, black). n = 6 to 8 animals, scale bars = 100 μm, 40×. (B) Lungs from parallel experiments were assessed for total CFU (n = 6 to 8 animals). (C) CEA10 and W72310 live conidia were incubated with primary bone marrow-derived macrophages for 1 or 4 h, and CFU were quantified. Data are represented as percent survival of 4 h/1 h. Data include 3 independent experiments. C57BL/6 mice were oropharyngeally inoculated with 3.0 × 10^7 AF633-stained mRFP-CEA10 or mRFP-W72310 conidia for 36 h. (D to F) Lungs were analyzed by flow cytometry for percent phagocytosis of conidia in immune cells (AF633+/CD45+) (D), percent positive conidia (AF633) in neutrophils and macrophages (E), and total neutrophils (CD45+/Ly6G+/CD11b+) and macrophages (CD45+/Ly6G−/CD11b+/CD64+) (F). (G and H) Viability of conidia phagocytosed in neutrophils and macrophages was analyzed by flow cytometry (G) and quantified (H). Representative micrographs were selected out of 6 mice per group. Mann-Whitney single comparisons were used. ns, P > 0.05; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.