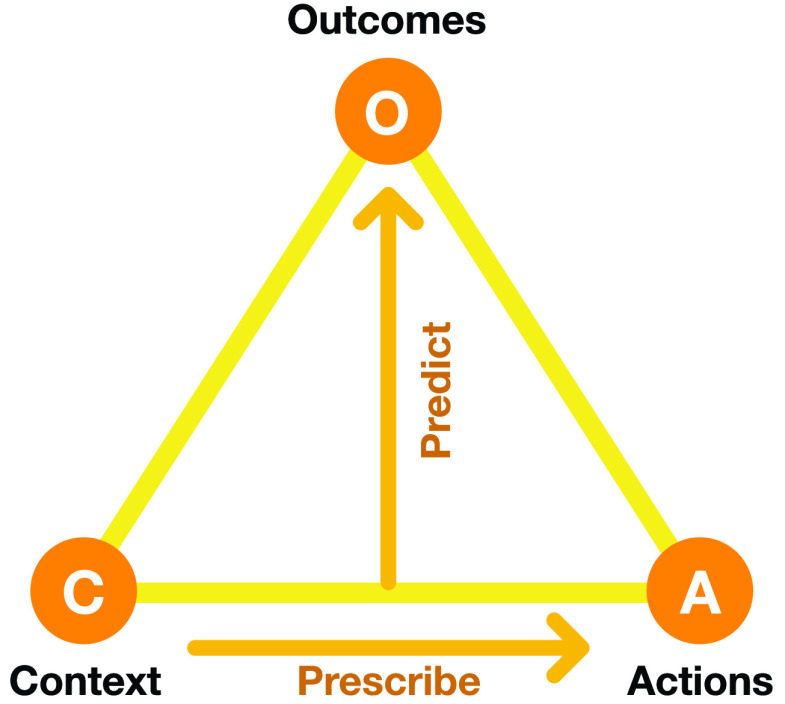
Fig. 1.
Elements of the ESP decision optimization method. A predictor is trained with historical data on how given actions in given contexts led to specific outcomes. For instance in the NPI optimization problem, given the state of pandemic in a particular country and the NPIs in effect, it predicts the future number of cases and the cost of the NPIs. The Predictor can be any machine learning model trained with supervised methods, such as a random forest or a neural network, or even a simulation, such as an epidemiological model. The Predictor is then used as a surrogate in order to evolve a Prescriptors, i.e., neural networks that implement decision policies (i.e., NPIs) resulting in best possible outcomes. With multiple conflicting objectives (such as cases and cost), evolution results in multiple Prescriptors, each representing a different tradeoff, from which a human decision maker can choose the ones that best matches their preferences.