TABLE II. Performance Comparison of NPI-LSTM Predictor With Baselines.
| Method | Norm. Case | Raw Case | Mean Rank | 1-step
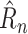
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | 2.47±1.22 | 1089126±540789 | 3.19±0.09 | 0.769±0.033 |
| RF | 0.95±0.05 | 221308±8717 | 1.98±0.10 | 0.512±0.000 |
| SVR | 0.71±0.00 | 280731±0 | 1.76±0.09 | 0.520±0.000 |
| Linear | 0.64±0.00 | 176070±0 | 1.63±0.09 | 0.902±0.000 |
| NPI-LSTM | 0.42±0.04 | 154194±14593 | 1.46±0.08 | 0.510±0.001 |
This table shows results along the four metrics described in Section V-B with mean and standard error over 10 trials. Interestingly, although RF and SVR do quite well in terms of the loss they were trained on (1-step
 MAE), the simple linear model outperforms them substantially on the metrics that require forecasting beyond a single day, showing the difficulty that off-the-shelf nonlinear methods have in handling such forecasting. In contrast, with the extensions developed specifically for the epidemic modeling case, the NPI-LSTM methods outperforms the baselines on all metrics.
MAE), the simple linear model outperforms them substantially on the metrics that require forecasting beyond a single day, showing the difficulty that off-the-shelf nonlinear methods have in handling such forecasting. In contrast, with the extensions developed specifically for the epidemic modeling case, the NPI-LSTM methods outperforms the baselines on all metrics.
