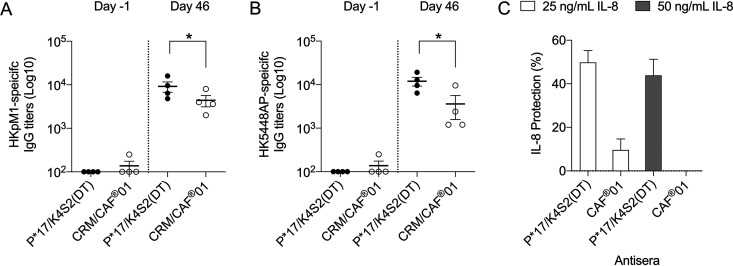
FIG 6.
Functionality of vaccine-induced antibodies. (A and B) Binding of P*17/K4S2(CRM) antibodies to S. pyogenes. Nunc MaxiSorp ELISA plates were coated with 200 μg/ml of heat-killed (HK) pM1 and 5448AP. P*17/K4S2(CRM) or CRM/CAF®01 antiserum were assessed. Vaccine antibodies specific for HKpM1 (A) and HK5448AP (B) were detected using HRP-conjugated rat secondary IgG antibody. The endpoint titer was defined as the highest dilution that gave an absorbance of >3 standard deviations above the mean absorbance of negative control wells. Mean ± SEM of individual titers of sera collected from days −1 (n = 4) and 46 (n = 4) are shown. Statistical analysis was performed using a nonparametric, unpaired Mann-Whitney U test (one-tailed) to compare groups (*, P < 0.05). (C) IL-8 protection by vaccine antisera. Cell-free culture supernatant from covR/S MT S. pyogenes strain 5448AP was coincubated with 50 ng/ml or 25 ng/ml of rIL-8 and antisera from P*17/K4S2(CRM) or CAF®01 vaccinated mice for 16 h at 37°C. In a parallel experiment, cell-free culture supernatant was preincubated with test antisera prior to coincubation with IL-8. Pooled data from both experiments are shown. Spy-CEP antiserum and naive serum were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Uncleaved IL-8 was measured by a Quantikine ELISA and is shown as IL-8 protection. The percentage protection values have been normalized to the positive- and negative-control sera (Spy-CEP = 100% and naive = 0%).