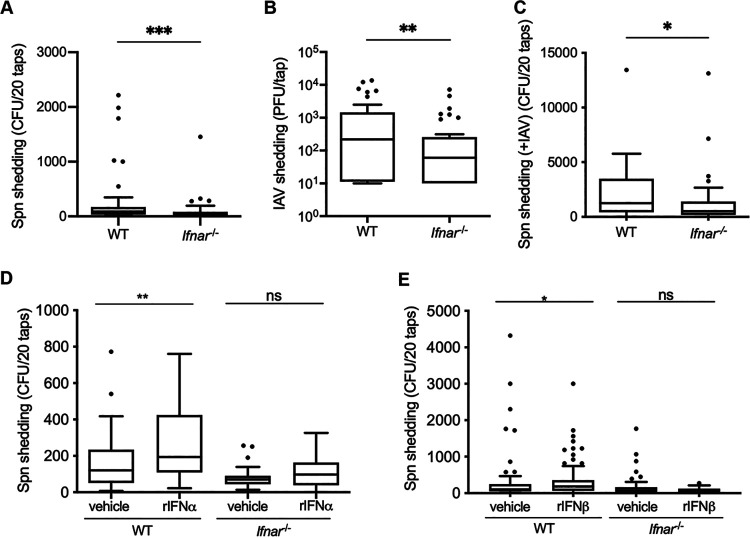
FIG 1.
Type I interferon is necessary for and promotes high-level shedding of S. pneumoniae and IAV. WT and Ifnar1−/− pups were infected i.n. with 103 CFU S. pneumoniae (Spn), 250 PFU IAV-x31, or S. pneumoniae plus IAVx31. (A and B) Ifnar1−/− pups shed significantly fewer bacteria than WT pups (A), and Ifnar1−/− pups shed significantly less IAV than WT pups (B). (C) WT and Ifnar1−/− pups first received IAV and then S. pneumoniae. Ifnar1−/− pups shed significantly fewer bacteria than WT pups. (D and E) Exogenous recombinant IFN-α2 or IFN-β increase pneumococcal shedding from WT but not Ifnar1−/− mice. WT and Ifnar1−/− pups were infected i.n. with 103 CFU S. pneumoniae and daily received either 1,000 IU of recombinant mouse IFN-α2 or 1,000 to 5,000 IU of recombinant mouse IFN-β or vehicle control (0.1% BSA-PBS) by i.n. instillation. Treatment of WT pups with rIFN-α2 (D) or rIFN-β (E) was sufficient to increase pneumococcal shedding over the baseline. Shedding data are shown as a Tukey box-and-whisker plot, with outliers shown as symbols. Each symbol represents the value from an individual pup on a single day. n ≥ 8 pups/group. ns, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (Mann-Whitney test).