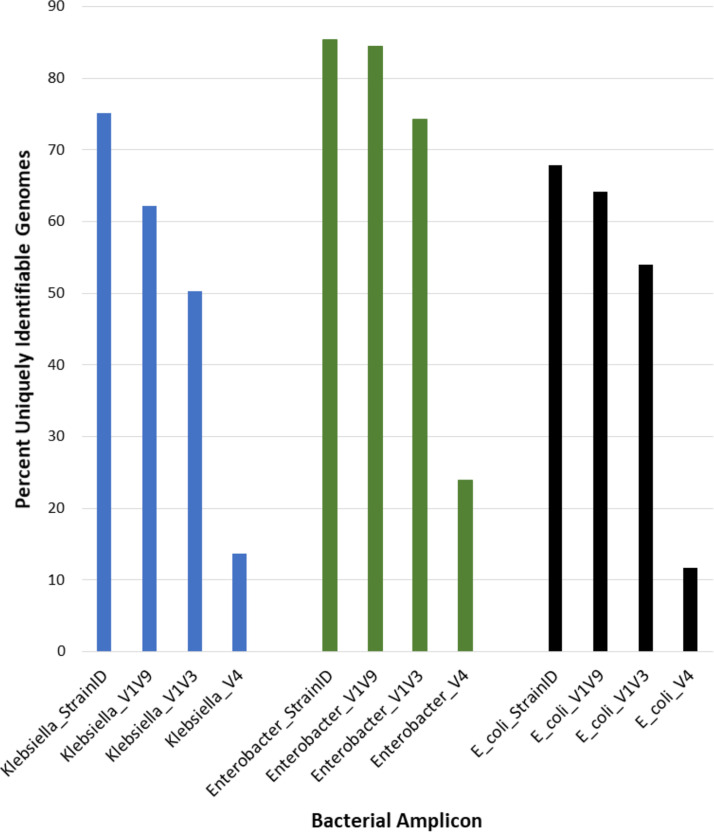
FIG 6.
Uniquely identifiable Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and E. coli genomes in the Athena database. Amplicon sequences were compared for 458 Klebsiella, 109 Enterobacter, and 187 E. coli genome entries in the Athena database. Each Klebsiella and Enterobacter genome ID contained up to eight contiguous 16S-23S gene pairs, and E. coli contained up to seven, from which the sequences of the V4, V1-V3, V1-V9, and StrainID amplicons were extracted. A genome ID was considered unique if it contained either a unique amplicon or a unique combination of amplicons. The percentage of uniquely identifiable genomes is shown on the y axis, and the taxonomy and amplicon type are shown on the y axis.