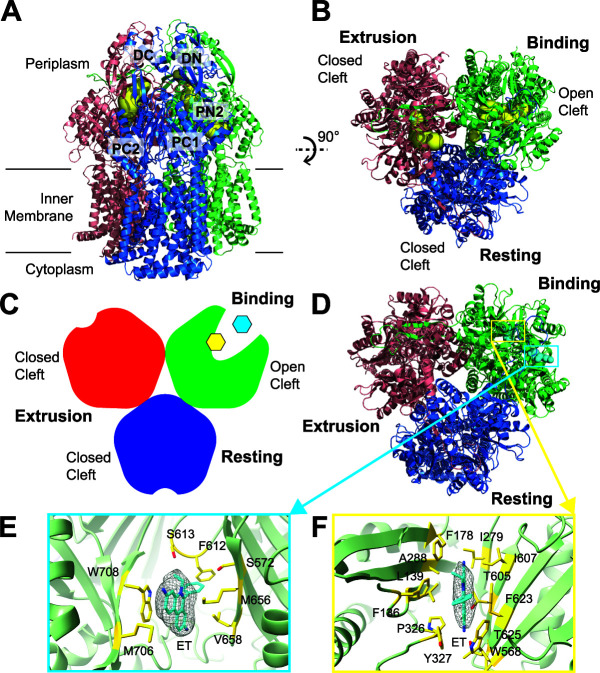
FIG 3.
Cryo-EM structure of AdeB-Et-II. (A) Ribbon diagram of the structure of AdeB-Et-II viewed in the membrane plane. (B) Ribbon diagram of the structure of AdeB-Et-II viewed from the extracellular space (top view). In panels A and B, the binding, extrusion, and resting protomers of AdeB are colored green, pink, and blue, respectively. The binding and extrusion channels are colored yellow. No channel is observed in the periplasmic domain of the resting protomer. (C) A cartoon representing the structure of the AdeB trimer viewed from the extracellular space. The binding, extrusion, and resting protomers of AdeB are colored green, red, and blue, respectively. The two bound Et ligands in the binding protomer are colored cyan (at the entrance binding site) and yellow (at the distal binding site). (D) Top view of the AdeB trimer depicting two bound Et ligands located at the binding protomer. The binding, extrusion, and resting protomers of AdeB are colored green, pink, and blue, respectively. The two bound Et ligands are depicted as cyan spheres. (E and F) The Et binding sites. Shown is an enlarged view of the entrance (E) and distal (F) sites. The EM densities of bound Et ligands are shown as gray meshes. The bound Et ligands are represented as cyan sticks. Residues that are involved in Et binding are represented as yellow sticks. The secondary structural elements of the binding protomer are depicted as green ribbons.