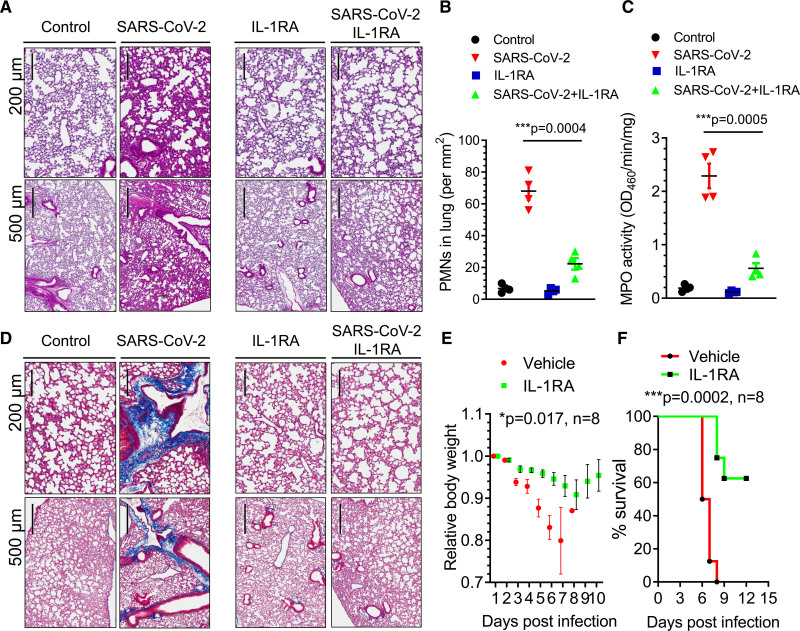
Figure 5.
IL (interleukin)-1 receptor blockade mitigates SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2)–induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, fibrosis, and mortality in K18-ACE-2 mice. K18-hACE-2 mice (2 mo old) were infected with a lethal dose of SARS-CoV-2 (1×105 p.f.u.). Mice also received the IL-1RA (IL-1 receptor antagonist) anakinra (10 mg/kg per d) or vehicle by IP (intraperitoneal) injection at 24 h post-infection and daily thereafter. A, Lung histopathology in K18-hACE-2 mice post-inoculation. Hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections (scale bars, 200 and 500 µm) showed inflammatory infiltrates composed of lymphocytes and polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs). Representative images from 2 independent experiments are shown. B, PMN numbers in lung were morphometrically quantified (n=4). Two-tailed unpaired t test (n=4). ***P<0.001. C, Lung PMN infiltration determined by measurement of lung tissue MPO (myeloperoxidase) activity (n=4). Two-tailed unpaired t test (n=4). ***P<0.001. D, Lung collagen deposition (blue) post–SARS-CoV-2 infection and the effects of IL-1RA treatment evaluated by Masson trichrome staining. Representative images from 2 independent experiments are shown (scale bars, 200 and 500 µm). E, Body weight of mice was monitored post–SARS-CoV-2 inoculation. IL-1RA treatment prevented weight loss. Two-tailed unpaired t test (n=8). *P<0.05. F, Survival of mice post–SARS-CoV-2 infection presented as a Kaplan-Meier plot. IL-RA treatment markedly improved survival. ***P<0.001. n=8.