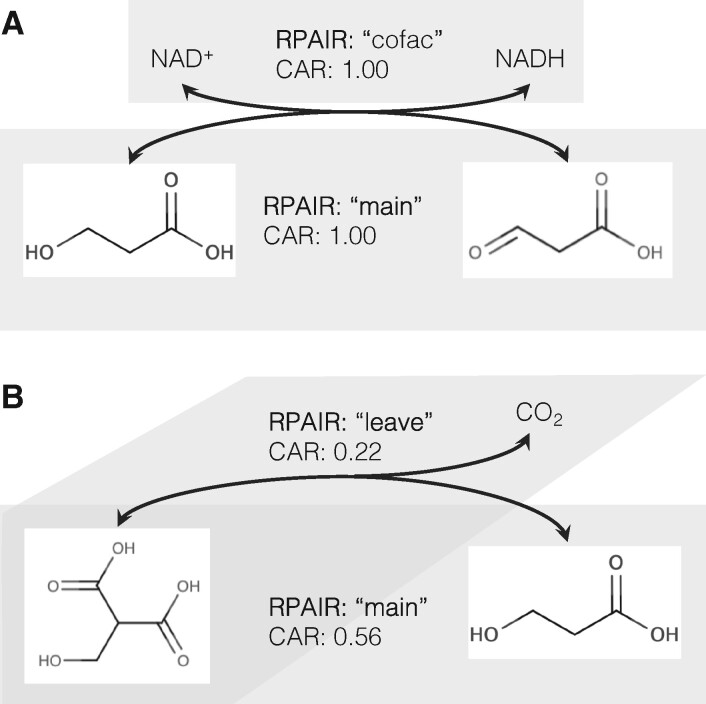
Fig. 2.
Example of relation between KEGG RPAIRs and the CAR value in a biochemical reaction. (A) Alcohol dehydrogenase: in an oxidoreduction reaction only electrons and protons are exchanged between the reaction participants, resulting in two distinct substrate-product pairs with a maximum CAR value. (B) Decarboxylation reaction: the atoms of the reactant are distributed between a leaving CO2 molecule with a low CAR value and a product molecule with a higher CAR value corresponding to the ‘main’ RPAIR