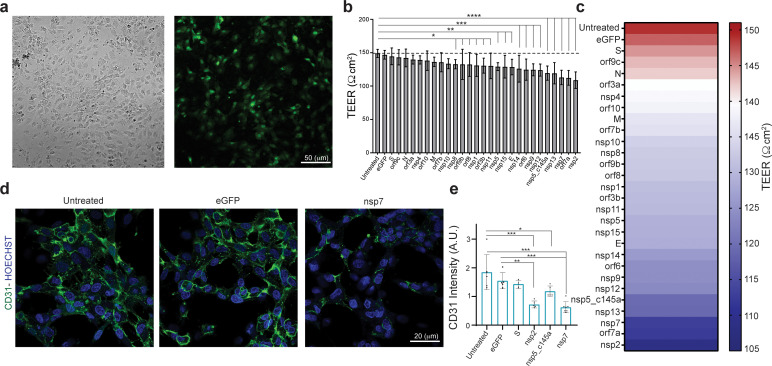
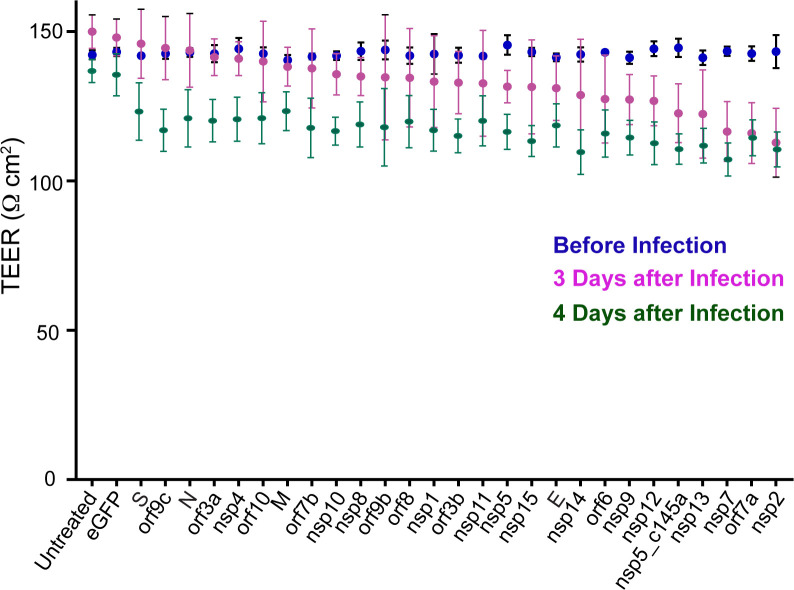
Figure 2. Effect of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV-2 proteins on human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) at day 3.
(a) Bright-field and fluorescent image of infected eGFP HUVEC, scale bar: 50 µm; (b) changes in barrier functions as a result of SARS-CoV-2 proteins were assessed by trans-epithelial-endothelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurement. Note the statistical differences compared to the untreated control condition, assessed by F-statistic with two-way ANOVA test, followed by the Holm–Sidak test for multiple comparisons; (c) color map showing a gradual decrease in TEER values compared to the untreated condition at day 3; (d) immunocytochemistry (ICC) for CD31 (green) and Hoechst (blue) for the three specified conditions, scale bar: 20 µm; (e) analysis of CD31 expression levels.