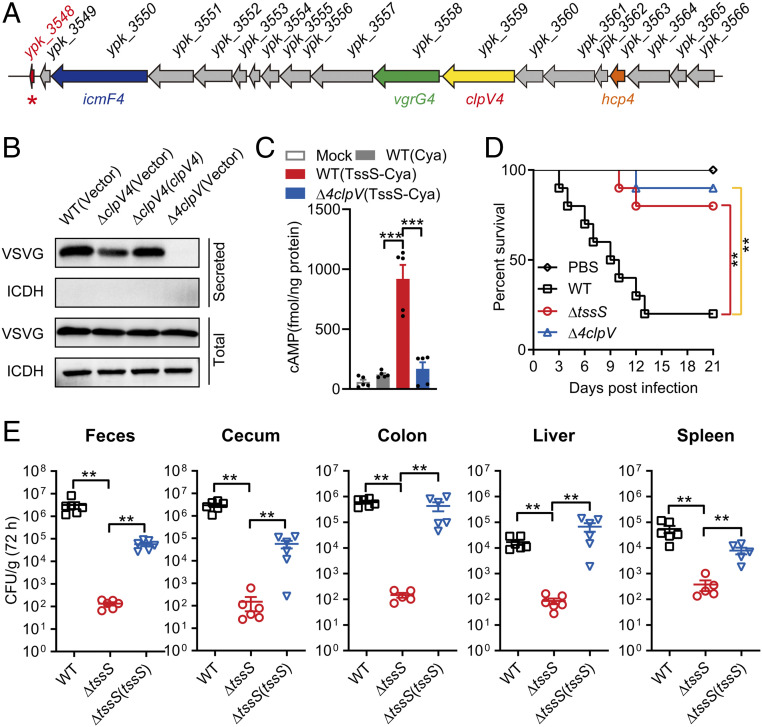
Fig. 1.
A T6SS-secreted micropeptide contributes to Yptb virulence. (A) Structure of the Yptb T6SS4 gene cluster. The tssS gene (ypk_3548) is indicated with a red asterisk. (B) TssS is a T6SS4 effector. An immunoblot analysis of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein (VSVG)-tagged TssS protein levels in culture supernatant of the relevant Yptb strains is shown. The cytoplasmic protein isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH) was used as a loading control and lysis control for the total and secreted fractions. (C) Raw264.7 cells were mock infected or infected with indicated Yptb strains expressing Cya-fused TssS at a multiplicity of infection of 20 for 2 h. Cyclic AMP present in lysates was measured. (D) C57BL/6 mice were intragastrically inoculated with Yptb WT, Δ4clpV, or ΔtssS. The survival rate of the mice was determined. (E) C57BL/6 mice were intragastrically inoculated with Yptb WT, ΔtssS, or ΔtssS(tssS). Homogenates of different tissues were plated to determine the bacterial CFU count per gram of organs at 72 h postinfection. Error bars represent ± SEM; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.